4.1: Letters
- Page ID
- 151324
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)In this section, you will be able to:
- Read, write, and type the letters ( ر ز س ش ص ض ة (التاء المربوطة in their different shapes.
- Pronounce the letters with ( ر ز س ش ص ض ة (التاء المربوطة short and long vowels.
The letters
This table shows the letters discussed on this page and includes an audio recordings of each letter's pronounciation
| Letter Name اسم الحرف |
Letter shape شكل الحرف |
Audio Recording |
|---|---|---|
| Raa | ر |
|
| Zai | ز |
|
| Seen | س |
|
| Sheen | ش |
|
| Saad | ص |
|
| Daad | ض |
|
The Letter Raa ر
In this section you will learn how to pronounce these 6 Arabic letters ر ز س ش ص ض and their articulation with their short and long vowels
Pronunciation of The Letter Raa ر
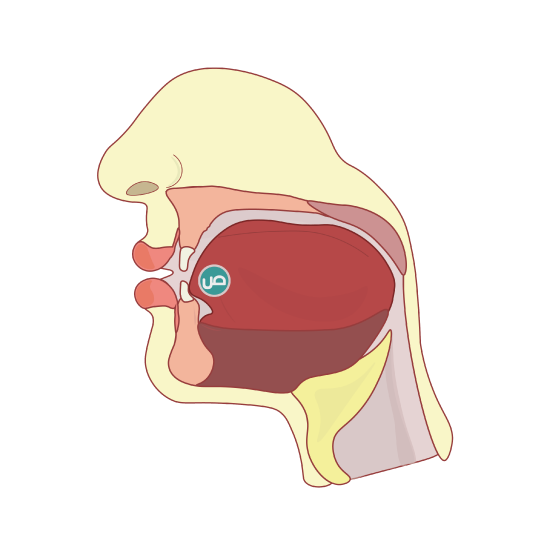
The letter “ر” is emitted from the tip of the tongue and what lies opposite to it of the gums of the two front top incisors (the plate). The tip with the top of the tongue needs to strike the gum to produce this sound correctly. The letters NOON and RAA “ر” come from the same articulation point, but the only difference is that the RAA “ر” uses the tip of the line and does not touch it. There is a small gap between the tongue and the gum and vibrate (trilling ) for Raa “ر” pronunciation. The main character of the RAA “ر” is that swing between “Tafkheem” and “Tarqeek”. “Tafkheem” is the opposite of “Tarqeek”. Raa “ر” depends on the short vowel that precedes it; if the short vowel is fathah or dhamah, then the letter Raa’s pronunciation will be stronger (Tafkheem). If the short vowel is kasrah, then the letter Raa’s “ر” pronunciation will be weaker (Tarqeek). (See Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\))
The Letter ر with the short vowels and sukun
|
The sound with sukun |
The sound with dhamah |
The sound with kasrah |
The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
|
رْ |
رُ |
رِ |
رَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
|
رو |
ري | را |
Find the letter Raa "ر " with the fatha
رُ - رِ - ر - رَ - رُ - را - ري - رو
- Answer
-
رَ
Writing Letter ر
This letter "ر" is a non-connector. It has only one connector like the letters "و", "ذ", "د", and "ا". The Raa "ر" is written almost entirely below the line. To write the initial "ر" begin on the line and curve downward below it. The letter "ر" looks like the shape of a crescent moon or a banana. To write a "ر" that is connected from a preceding letter, start from the connecting segment on the line, and then curve down.
| Final Form | Medial Form | Initial Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ر/ ـر | ـر | ر | ر |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter "Raa" ر
The Letter Zai ز
This letter corresponds to the English sound “z” as in the word “zebra”.
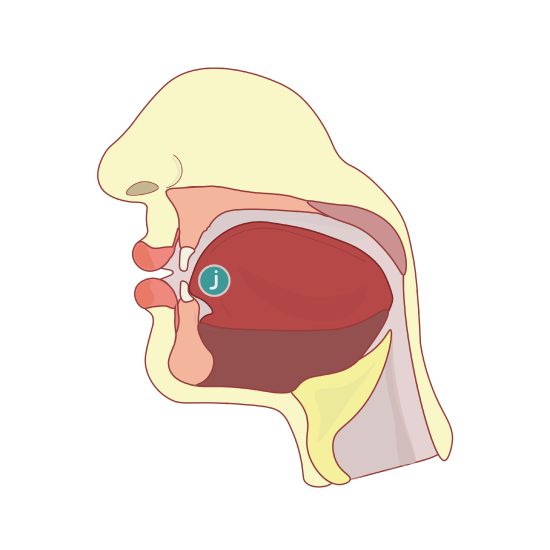
The articulation place of the letter “ز” is the tongue and the top edge of the two frontal lower incisors. There is a little space left in between the tip of the tongue and the plates of the teeth when pronouncing this letter. In other words, the tip of the tongue just misses the edge of the top and lower teeth. When this letter is emitted, a light whistle-like sound should be heard accompanying the sound, which is called in Arabic “Safeer, صفير”. The most common mistake when pronouncing this letter is pressing the tongue up against the plates of the teeth causing the sound to be suppressed when attempting to say the letter. (see Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).
|
The sound with sukun |
The sound with dhamah |
The sound with kasrah |
The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
| زْ | زُ | زِ | زَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
| زو | زي | زا |
Highlight the letter Zai " ز" in the following words:
- خبز - زار - أرز - زينة - حزب
- Answer
-
خبز - زار - أرز - زينة - حزب
Writing Letter ز
You write the letters "ز" in the same way you write the letter "ر." The only difference is the letter "ز" has a dot above it. (Watch the video)
| Final Form | Medial Form | Initial Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ز / ـز | ـز | ز | ز |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter Zay
The Letter Seen س
The letter “Seen” “س” is the name of the Arabic letter that corresponds to English “s”, as in the word seen itself. However, remember that English “s” is often pronounced as “z”, such as in “easy” and “optimism”, and in many plurals like “dogs”. Arabic “س”, on the other hand, always retains the soft “s” sound. “س” is a frontal consonant, which means that surrounding vowels take a frontal quality, especially Alif (the long vowel), and fathah, which sound like the “e” in bet.
The articulation point of the letter “س” is the tongue and the tip top edge of the two frontal low incisors. There is a space left in between the tip of the tongue and the plates of the teeth when pronouncing this letter. A whistle-like sound should accompany its pronunciation. (See Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\))
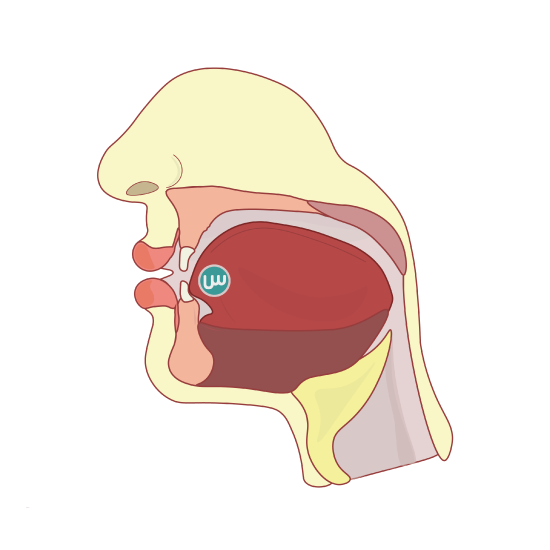
|
The sound with sukun |
The sound with dhamah |
The sound with kasrah |
The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
| سْ | سُ | سِ | سَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
| سو | سي | سا |
Find the long vowels of the letter Seen "س" in the following words:
سيَّارة - سارَ - حساب - أسير- خَس - أسْوَد
- Answer
-
سار - حساب - أسير
Writing Letter س
The letter "س" is a connecting letter distinguished in print by its three teeth. In handwriting, the letter "س" is often written without its teeth (as straight line). To write the independent "س", begin on the line and draw a tiny hook and three teeth (like a toothbrush) then dip below the line into the tail, almost like a semicircle. In the beginning of the word, "ســــ" is written like independent "س", but without the tail - the segment should be longer to distinguish the letter.
When "س" is connected to a preceding letter, the connecting segment and the body of the letter are indistinguishable, and there is no hook in the beginning. This means that the connecting segment and the letter should form a line like this "ــســـــ". The body should be long enough to distinguish it from a connecting segment.
The final "ـــس" is written with a tail, which must come all the way back up to the line. (Watch the video)
| Independent Form | Independent Form | Independent Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ـس | ـس | ـس | ـس |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter Seen
The Letter Sheen ش
The letter “ش” articulation point is the middle of the tongue and what lies opposite to it from the roof of the mouth of the hard palate – similar to the letter “ج” and the consonant “ي,” but it has specific characteristics. The letter “ش” is similar to the English sound “sh” in the words “should, shall, she”. (see Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\))
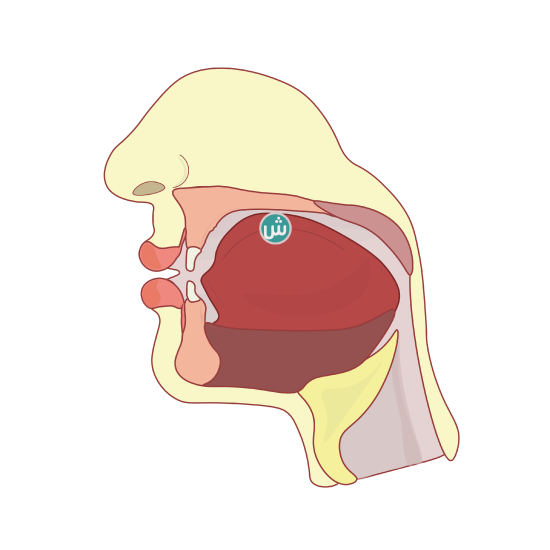
| The sound with sukun | The sound with dhamah | The sound with kasrah | The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
| شْ | شُ | شِ | شَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
| شو | شي | شا |
Find the long vowels of the letter Sheen ش
- شَ - شو - شُ - شِ - شا - شي
- Answer
-
شو - شا - شي
Writing Letter ش
You write the letter Sheen "ش" in the same way you write the letter Seen "س", but with the addition of three dots over the three teeth. The three dots are connected in handwriting and take the shape of the overturned letter "v". (Watch the video)
| Final Form | Medial Form | Initial Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ـش | ـشـ | شــ | ش |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter Sheen
The Letter Saad ص
The articulation place of the letter “Saad” “ص” is the same as the letter “س” from the tip of the tongue and the top edge of the two front lower incisors. However, this letter represents the emphatic counterpart of “س”. Pronounce “س” out loud and note the position of your tongue. It should be toward the front and close to the roof of the mouth. Now, starting at the back of your teeth, move your tongue back along the roof of your mouth. You will find a bony ridge just behind the teeth, before the upward curve of the roof of your mouth; place your
tongue against this ridge. The rest of tongue will drop lower inside your mouth to gather air. The emphatic consonants in Arabic are pronounced by placing the end of the tongue in this spot and dropping the rest of the tongue as low as you can. (see Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)).
| The sound with sukun | The sound with dhamah | The sound with kasrah | The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
| صْ | صُ | صِ | صَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
| صو | صي | صا |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter Saad
Which of the following is the Arabic letter "ص"
Seen - Sheen - Saad - Zai - Raa
- Answer.
- Saad
Writing Letter ص
The letter “ص” is a connector letter and retains the same basic shape in both print and handwriting. There are two essential points to keep in mind when writing “ص”. First, the loop must be large and oval-shaped. Secondly, there should be a small tooth after the loop.
To write the independent “ص”, start on the line and make a big loop up and back to your right, then swing down and close it. Without stopping, make the tooth, then drop well below the line to make the tail. The tail of “ص” is the same shape of the tail of “س” and must come all the way back up to the line.
The letter in the beginning of the word, “صــ”, is written in the same way, but without the tail. After making the tooth, continue to the connecting segment. To write the middle “ــصـــ” connected from a previous letter, draw the connecting segment to the starting point of the loop, the same point at which you started in the initial position, and then follow the same steps. At the end of the word, “ــص” is connected in the same way as the medial “ــصــ” and ends with a tail.
| Final Form | Medial Form | Initial Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ـص | ـصـ | صـ | ص |
The Letter Daad ض
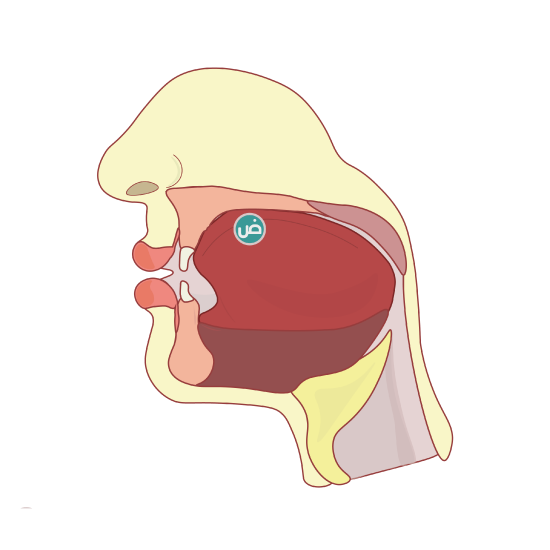
The letter Daad “ض” is articulated from the one or both sides of the tongue and from the molars and the gum area next to the molars. This letter can be articulated from one side (right or left) of the tongue alone, or from both sides of the tongue simultaneously, which is more difficult. “ض” has the characteristic of compression of the sound, as well as tafkheem (elevated/heaviness), so the deep part of the tongue raises when pronouncing it and compresses the sound at the same time. The “ض” represents the emphatic counterpart of “د”. To pronounce “ض”, place your your tongue in the same position as you did to say “ص” and “د”, and the result will be “ض”. (see Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\))
| The sound with sukun | The sound with dhamah | The sound with kasrah | The sound with Fathah |
|---|---|---|---|
| ضْ | ضُ | ضِ | ضَ |
| The letter with the long vowel "و" oo | The letter with the long vowel "ي" ee | The letter with the long vowel "ا" aa |
|---|---|---|
| ضو | ضي | ضا |
Find the short vowels of the letter Daad ض in the following:
ضُ - ضا - ضي - ضِ - ضْ- ضو - ضَ
- Answer
-
ضُ - ضِ - ضَ
Writing Letter ض
You write the letter “ض” in the same way as the letter “ص” and add a dot above the letter. (Watch the video)
| Final Form | Medial Form | Initial Form | Independent Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| ـض | ـضـ | ضـ | ض |
Watch the video to learn how to write the letter Daad
Watch the video to learn more about the letters:
Exercise 4.1.7:
Exercise 4.1.8:
Trace the letter in the initial, medial, final and independent positions ( remember to write from right to left):
Trace the letter ر (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| صورة | جار | خبـر | رنا |
Trace the letter ز (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| أرز | خبز | حزب | زوج |
Trace the letter س (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| درس | أوتوبيس | حساب | أستاذ |
Trace the letter ش (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| جرش | ريش | بشير | شاي |
Trace the letter ص (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| باص | شخص | فصل | صباح |
Trace the letter ض (remember to read and trace from right to left)
| Independent | Final | Medial | Initial |
| رَضَّ | أبيض | أخضر | ضرس |
Exercise 4.1.9:
Connect the letters to form the appropriate word. Make sure to write the correct form of the letter. (Remember to write from right to left)
Example:
ض + ر+ س = ضرس
| د + ا + ر |
| ج + ا + ر |
| خ + ب + ر |
| ب + ا + ر + د |
| ر + ب + ا + ب |
- Answer
-
دار
جار
خبر
بارد
رباب
| خ + ب + ز |
| ز + و + ج |
| أ + ر + ز |
| ز + ي + ت |
| ح + ز + ب |
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
خبز
زوج
أرز
زيت
حزب
| أ + س + ت + ا + ذ |
| أ + د + ر + س |
| أ + س + ر + + ة |
| ح + س + ا + ب |
| س + ي + ا + ر + ة |
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
أستاذ
أدرس
أسرة
حساب
سيارة
| ش + ا + ي |
| ش + ا + ب + ة |
| ب + ش + ي + ر |
| ج + ر + ش |
| ر + ي + ش |
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
شاي
شابة
بشير
جرش
ريش
| ب + ا + ص |
| ص + ب + ا + ح |
| ش + خ + ص |
| ص + ب + ر |
| أ + ص + ب + ح |
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
باص
صباح
شخص
صبر
أصبح
| أ + خ + ض + ر |
| أ + ب + ي + ض |
| ض + ج + ر |
|
ض + ب + ا + ب |
| ض + ر + س |
- Answer
-
Add texts here. Do not delete this text first.
أخضر
أبيض
ضجر
ضباب
ضرس
Section Three: Listening
Exercise 4.1.10:
In this section you will listen to the sound of the letters with short and long vowels, then write them
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ِAnswers
صُ
ضا
سي
سُ