Bede, Ecclesiastical History of the English People
- Page ID
- 108350
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Bede, Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum ("Ecclesiastical History of the English People"), c. 720s, Britain
The introduction has been prepared by John Terry (2021) and the translation comes from Bede, The Ecclesiastical History of the English Nation, trans. L.C. Jane's (New York E.P. Dutton, 1910). For a full online version, see https://sourcebooks.fordham.edu/basis/bede-book1.asp.
The excerpts below are in three sections with response questions at the beginning of each section.
2) Contents and Organization of the Ecclesiastical History
2) Conversion to Christianity: Practical Considerations
3) Conversion and Royal Policy: A Case Study of King Edwin of Northumbria
Introduction
1. Bede's Life and Context
Bede was a monk and scholar in Northumbria1 who wrote multiple works on history, exegesis,2 hagiography,3 theology, and other topics.
He was born around 672 or 673 and given by his family as a child oblate4 to the monastic community at Wearmouth-Jarrow in around 680 or 681. According to his own account, “I was born in the territory of this monastery. When I was seven years of age I was, by the care of my kinsmen, put into the charge of the reverend Abbot Benedict and then Ceolfrith, to be educated. From then on I have spent all my life in this monastery, applying myself entirely to the study of the Scriptures; and, amid the observance of the discipline of the Rule and the daily task of singing in the church, it has always been my delight to learn or to teach or to write.”5 Professor Michelle Brown helps fill out our picture of Bede’s daily life and progress as a monastic scholar:
Time was set . . . aside each day for personal prayer and meditative private reading of Scripture (lectio divina) and for manual labour, which might vary in accordance with the gifts of the individual. In Bede’s case, an unusually large allocation of time would have been devoted to his research and teaching activities. He would have taught in the schoolroom, no doubt following the sort of curriculum established in the Canterbury school of Theodore and Hadrian––two learned figures from the Mediterranean world––in the late seventh century. This included the study of Latin, Greek, theology, exegesis, computistics, astronomy, medicine, poetry, and Gregorian chant. The rest of his study time would have been spent in the library, which we can imagine containing large book cupboards (armaria) of the sort depicted in the Codex Amiatinus, stocked with volumes from the early Christian Meditarranean, Byzantium, the Christian Orient, Frankia, Ireland, and other parts of England. He would have laboured in the scriptorium, drafting his own works with a metal stylus on wax-covered tablets, copying his words or those of earlier authorities and of Scripture in a fine calligraphic hand onto prepared calfskin (vellum) with a goose-quill, using inks and pigments made from local mineral, plant, and animal extracts, prepared in the scriptorium by the monks themselves and their novice assistants.6

Despite probably never traveling very far from his home in northern Britain, Bede knew of the world and received an education similar to the best available in the Christian world. He read and wrote widely, and wrote a long historical account of the “English People” sometime by around 731 known as the Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum, or “The Ecclesiastical History of the English People.” This is easily Bede’s best-known work and “undeniably his life’s work.”7
Much of his historical vision is providential. In other words, he tells the history of his Islands through the lens of inexorable conversion to Christianity––specifically, a form of Christianity most closely aligned with the Roman papacy, the office of the pope in Rome. According to Bede, prior to the arrival of the Romans, Britain’s past had been murky and mired in “paganism,” or the worship of other, non-Christian deities. The Romans, though pagans in Bede’s eyes, brought a degree of civilization to Britain and, in the century of so prior to the Roman military’s departure in the early 400s, a modest process of Christianization. (The Roman emperor Constantine converted to Christianity in the early 300s and encouraged its spread in the empire.) Bede also credits the Roman Empire with the prestige that popes would come to inherit. The best evidence for this is his treatment of Augustine of Canterbury, a missionary commissioned by Pope Gregory I (d. 604) to convert the Britons, beginning with the southeastern kingdom of Kent. For Bede, Augustine exported Christianity and civilization to a pagan land through God’s own will.
It’s through this lens that Bede makes the most sense for us as modern readers: when he told stories about various saints and their miracles, for example, it’s clear that he expected his audience to be inspired by the examples of those saints. When he recorded the reigns of local monarchs (such as King Æthelberht below), he measured their achievements by the degree to which they had embraced Christianity as faith and policy.

2. Contents and Organization of the Ecclesiastical History
Bede’s narrative orbited around the lives of the best of the “English” (or Angli). At times he launches into miniature hagiographies, or saints’ lives, of various individuals responsible for spreading Roman-style Christianity in Britain. At other times he focuses on particularly effective (or corrupt) monarchs who can serve as exempla (or examples) for his audience.
Book I
1-12: The geography and history of Roman Britain c. 50 BC-AD 400., following the British historian Gildas, who wrote the only known narrative history of the period c. 400-550 in Britain.
13-22: Britain after Rome, the adventus Saxonum (or “arrival of the Saxons”), and the spread of Pelagian heresy, c. 400-597.8
23-34: The mission of Theodore and Hadrian sent by Pope Gregory I, the conversion of Æthelberht of Kent, and the initial spread of Christianity, c. 597-603.
Book II
1-14: Augustine and his bishops Mellitus and Justus work to spread orthodox practice, the spread of Christianity to Northumbria, and the conversion of Edwin of Northumbria, c. 604-627.
15-20: The spread of Christianity to Essex and Lindsey and the death of Edwin, c. 624-632/33.
Book III
1-14: The conversion of Oswald of Northumbria, the foundation of Lindisfarne by the Irish bishop Aidan, the conversion of the Picts, and the death of Oswald at Heavenfield, c. 633-642/43.
15-24: The life of bishop Aidan of Lindisfarne, the spread of monastic practice in East Anglia, the reign of Peada over the Middle Angles, the spread of monasticism in Essex by Cedd, the death of Penda and conversion of the Mercians, c. 643-655.
25-30: The Synod of Whitby concerning the correct date of Easter and other orthodox practices, and episcopal activities in Wessex, Northumbria and Wessex, c. 664-669.
Book IV
1-20: The consecration of Theodore and Hadrian, and their activities in England, c. 669-680.
21-30: Accounts of the lives of Hild (d. 680) and Cuthbert (d. 687)
Book V
1-14: The lives of Æthelwald, bishop John, Cædwalla of the West Saxons, the death of Theodore (d. 690), Egbert, Willibrord’s mission in Frisia, and the vision of Dryhthelm, c. 680-700.
15-22: The acceptance of the Roman Easter by the Irish churches, the lives of Adomnan, Cenred of Mercia, Offa of the East Saxons, Albinus (successor to Hadrian), c. 675-731.
23-24: Bede’s assessment of the present state of the English church, a chronological recapitulation of the Historia, and an autobiographical entry on his life and works.
Footnotes
[1] Northumbria was a region of the Britain that roughly corresponds with the modern county of Northumberland just south of Scotland. Its coast lies on the North Sea.
[2] Exegesis refers to interpretation of the Bible, and in the medieval Europe it was a common genre of literature among monastic scholars and clergy.
[3] Hagiography is a genre of medieval and modern literature that deals with the lives of saints, or very holy people. Hagiographic texts usually contain common elements or tropes, including miracle working, humility, mastery over nature and non-Christian enemies, and general imitatio Christi, or "imitation of Christ."
[4] This means that a family has given the gift of a child to a monastic institution, which could happen for a number of reasons ranging from the illegitimacy of the child to exhibiting promising scholarly potential, which was probably the reason Bede's family gave him as a child oblate to Wearmouth-Jarrow, on the North Sea coast of Nurthumbria.
[5] Historia Ecclesiastica book 5, chapter 24. It's conventional to use a short citation for Bede's Historia Ecclesiastica like this: HE 5.24.
[6] Michelle P. Brown, “Bede’s Life in Context,” in Scott DeGregorio, ed., The Cambridge Companion to Bede (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2010), 3-24, at 7-8.
[7] Scott DeGregorio, “The New Bede,” in Innovation and Tradition in the Writings of the Venerable Bede, ed. DeGregorio (Morgantown, WV: West Virginia University Press, 2006), 1-10, at 2.
[8] The Pelagian heresy refers to the teachings of the Romano-British scholar Pelagius, who taught, among other things, that salvation and perfection can be gained through good works. "Heresy" refers to anything that is not approved, mainline, or "orthodox" teaching of the church. Bede, as a follower of papal Christianity, rejected Pelagius as a heretic.
Excerpts
1) Migration and Change (HE 1.12-22) (return to top)
Response questions for this section:
1) How does Bede describe the various groups of people from this period of change? Why do you think this is?
2) What reasons does Bede give for the fall of the Roman empire in Britain?
3) What seems to be God's role in the events of this section?
CHAPTER XII
THE BRITONS, BEING RAVAGED BY THE SCOTS AND PICTS, SOUGHT SUCCOUR FROM THE ROMANS, WHO, COMING A SECOND TIME, BUILT A WALL ACROSS THE ISLAND; BUT THE BRITONS BEING AGAIN INVADED BY THE AFORESAID ENEMIES, WERE REDUCED TO GREATER DISTRESS THAN BEFORE
FROM that time, the south part of Britain, destitute of armed soldiers, of martial stores, and of all its active youth, which had been led away by the rashness of the tyrants, never to return, was wholly exposed to rapine, as being totally ignorant of the use of weapons. Whereupon they suffered many years under two very savage foreign nations, the Scots from the west, and the Picts1 from the north. We call these foreign nations, not on account of their being seated out of Britain, but because they were remote from that part of it which was possessed by the Britons; two inlets of the sea lying between them, one of which runs in far and broad into the land of Britain, from the Eastern Ocean, and the other from the Western, though they do not reach so as touch one another. The eastern has in the midst of it the city Giudi. The western has on it, that is, on the right hand thereof, the city Alcluith, which in their language signifies the Rock Cluith, for it is close by the river of that name.
On account of the irruption of these nations, the Britons sent messengers to Rome with letters in mournful manner, praying for succours, and promising perpetual subjection, provided that the impending enemy should be driven away. An armed legion was immediately sent them, which, arriving in the island, and engaging the enemy, slew a great multitude of them, drove the rest out of the territories of their allies, and having delivered them from their cruel oppressors, advised them to build a wall between the two seas across the island, that it might secure them, and keep off the enemy; and thus they returned home with great triumph. The islanders raising the wall, as they had been directed, not of stone, as having no artist capable of such a work, but of sods, made it of no use. However, they drew it for many miles between the two bays or inlets of the seas, which we have spoken of; to the end that where the defense of the water was wanting, they might use the rampart to defend their borders from the irruptions of the enemies. Of which work there erected, that is, of a rampart of extraordinary breadth and height, there are evident remains to be seen at this day. It begins at about two miles' distance from the monastery of Abercurnig, on the west, at a place called in the Pictish language, Peanfahel, but in the English tongue, Penneltun, and running to the westward, ends near the city Alcluith.
But the former enemies, when they perceived that the Roman soldiers were gone, immediately coming by sea, broke into the borders, trampled and overran all places, and like men mowing ripe corn, bore down all before them. Hereupon messengers are again sent to Rome, imploring aid, lest their wretched country should be utterly extirpated, and the name of a Roman province, so long renowned among them, overthrown by the cruelties of barbarous foreigners, might become utterly contemptible. A legion is accordingly sent again, and, arriving unexpectedly in autumn, made great slaughter of the enemy. obliging all those that could escape, to flee beyond the sea; whereas before, they were wont yearly to carry off their booty without any opposition. Then the Romans declared to the Britons, that they could not for the future undertake such troublesome expeditions for their sake, advising them rather to handle their weapons like men, and undertake themselves the charge of engaging their enemies, who would not prove too powerful for them, unless they were deterred by cowardice; and, thinking that it might be some help to the allies, whom they were forced to abandon, they built a strong stone wall from sea to sea, in a straight line between the towns that had been there built for fear of the enemy, and not far from the trench of Severus. This famous wall, which is still to be seen, was built at the public and private expense, the Britons also lending their assistance. It is eight feet in breadth, and twelve in height, in a straight line from east to west, as is still visible to beholders. This being finished, they gave that dispirited people good advice, with patterns to furnish them with arms. Besides, they built towers on the seacoast to the southward, at proper distances, where their ships were, because there also the irruptions of the barbarians were apprehended, and so took leave of their friends, never to return again.
After their departure, the Scots and Picts, understanding that they had declared they would come no more, speedily returned, and growing more confident than they had been before, occupied all the northern and farthest part of the island, as far as the wall. Hereupon a timorous guard was placed upon the wall, where they pined away day and night in the utmost fear. On the other side, the enemy attacked them with hooked weapons, by which the cowardly defenders were dragged from the wall, and dashed against the ground. At last, the Britons, forsaking their cities and wall, took to flight and were dispersed. The enemy pursued, and the slaughter was greater than on any former occasion; for the wretched natives were torn in pieces by their enemies, as lambs are torn by wild beasts. Thus, being expelled their dwellings and possessions, they saved themselves from starvation, by robbing and plundering one another, adding to the calamities occasioned by foreigners, by their own domestic broils, till the whole country was left destitute of food, except such as could be procured in the chase.
CHAPTER XIII
IN THE REIGN OF THEODOSIUS THE YOUNGER, PALLADIUS WAS SENT TO THE SCOTS THAT BELIEVED IN CHRIST; THE BRITONS BEGGING ASSISTANCE OF ÆTIUS, THE CONSUL, COULD NOT OBTAIN IT. [A.D. 446.]
CHAPTER XIV
THE BRITONS, COMPELLED BY FAMINE, DROVE THE BARBARIANS OUT OF THEIR TERRITORIES; SOON AFTER THERE ENSUED PLENTY OF CORN, LUXURY, PLAGUE, AND THE SUBVERSION OF THE NATION. [A.D. 426-447.]
IN the meantime, the aforesaid famine distressing the Britons more and more, and leaving to posterity lasting memorials of its mischievous effects, obliged many of them to submit themselves to the depredators; though others still held out, confiding in the Divine assistance, when none was to be had from men. These continually made excursions from the mountains, caves, and woods, and, at length, began to inflict severe losses on their enemies, who had been for so many years plundering the country. The Irish robbers thereupon returned home, in order to come again soon after. The Picts, both then and afterwards, remained quiet in the farthest part of the island, save that sometimes they would do some mischief, and carry off booty from the Britons.
When however, the ravages of the enemy at length ceased, the island began to abound with such plenty of grain as had never been known in any age before; with plenty, luxury increased, and this was immediately attended with all sorts of crimes; in particular, cruelty, hatred of truth, and love of falsehood; insomuch, that if any one among them happened to be milder than the rest, and inclined to truth, all the rest abhorred and persecuted him, as if he had been the enemy of his country. Nor were the laity only guilty of these things, but even our Lord's own flock, and his pastors also, addicting themselves to drunkenness, animosity, litigiousness, contention, envy, and other such like crimes, and casting off the light yoke of Christ. In the meantime, on a sudden, a severe plague fell upon that corrupt generation, which soon destroyed such numbers of them, that the living were scarcely sufficient to bury the dead: yet, those that survived, could not be withdrawn from the spiritual death, which their sins had incurred, either by the death of their friends, or the fear of their own. Whereupon, not long after, a more severe vengeance, for their horrid wickedness, fell upon the sinful nation. They consulted what was to be done, and where they should seek assistance to prevent or repel the cruel and frequent incursions of the northern nations; and they all agreed with their King Vortigern to call over to their aid, from the parts beyond the sea, the Saxon nation; which, as the event still more evidently showed, appears to have been done by the appointment of our Lord Himself, that evil might fall upon them for their wicked deeds.
CHAPTER XV
THE ANGLES, BEING INVITED INTO BRITAIN, AT FIRST OBLIGED THE ENEMY TO RETIRE TO A DISTANCE; BUT NOT LONG AFTER, JOINING IN LEAGUE WITH THEM, TURNED THEIR WEAPONS UPON THEIR CONFEDERATES. [A.D. 450-456.]
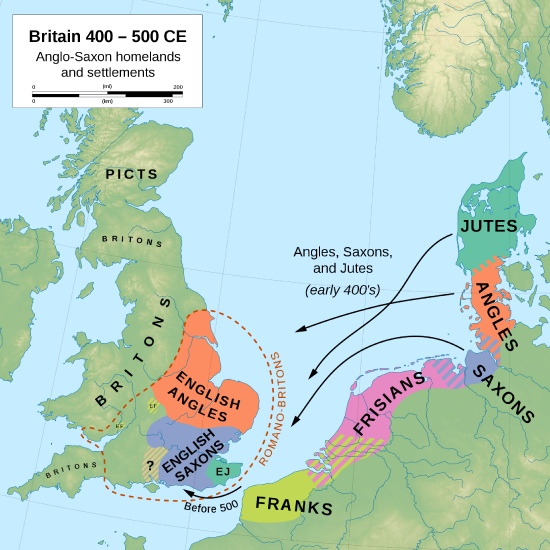
IN the year of our Lord 449, Martian being made emperor with Valentinian, and the forty sixth from Augustus, ruled the empire seven years. Then the nation of the Angles, or Saxons, being invited by the aforesaid king, arrived in Britain with three long ships, and had a place assigned them to reside in by the same king, in the eastern part of the island, that they might thus appear to be fighting for their country, whilst their real intentions were to enslave it. Accordingly they engaged with the enemy, who were come from the north to give battle, and obtained the victory; which, being known at home in their own country, as also the fertility of the country, and the cowardice of the Britons, a more considerable fleet was quickly sent over, bringing a still greater number of men, which, being added to the former, made up an invincible army. The newcomers received of the Britons a place to inhabit, upon condition that they should wage war against their enemies for the peace and security of the country, whilst the Britons agreed to furnish them with pay. Those who came over were of the three most powerful nations of Germany Saxons, Angles, and Jutes. From the Jutes are descended the people of Kent, and of the Isle of Wight, and those also in the province of the West Saxons who are to this day called Jutes, seated opposite to the Isle of Wight. From the Saxons, that is, the country which is now called Old Saxony, came the East Saxons, the South Saxons, and the West Saxons. From the Angles, that is, the country which is called Anglia, and which is said, from that time, to remain desert to this day, between the provinces of the Jutes and the Saxons, are descended the East Angles, the Midland Angles, Mercians, all the race of the Northumbrians, that is, of those nations that dwell on the north side of the river Humber, and the other nations of the English. The two first commanders are said to have been Hengist and Horsa.5 Of whom Horsa, being afterwards slain in battle by the Britons, was buried in the eastern parts of Kent, where a monument, bearing his name, is still in existence. They were the sons of Victgilsus, whose father was Vecta, son of Woden; from whose stock the royal race of many provinces deduce their original. In a short time, swarms of the aforesaid nations came over into the island, and they began to increase so much, that they became terrible to the natives themselves who had invited them. Then, having on a sudden entered into league with the Picts, whom they had by this time repelled by the force of their arms, they began to turn their weapons against their confederates. At first, they obliged them to furnish a greater quantity of provisions; and, seeking an occasion to quarrel, protested, that unless more plentiful supplies were brought them, they would break the confederacy, and ravage all the island; nor were they backward in putting their threats in execution. In short, the fire kindled by the hands of these pagans proved God's just revenge for the crimes of the people; not unlike that which, being once lighted by the Chaldeans, consumed the walls and city of Jerusalem. For the barbarous conquerors acting here in the same manner, or rather the just Judge ordaining that they should so act, they plundered all the neighbouring cities and country, spread the conflagration from the eastern to the western sea, without any opposition, and covered almost every part of the devoted island. Public as well as private structures were overturned; the priests were everywhere slain before the altars; the prelates and the people, without any respect of persons, were destroyed with fire and sword; nor was there any to bury those who had been thus cruelly slaughtered. Some of the miserable remainder, being taken in the mountains, were butchered in heaps; others, spent with hunger, came forth and submitted themselves to the enemy for food, being destined to undergo perpetual servitude, if they were not killed even upon the spot some, with sorrowful hearts, fled beyond the seas. Others, continuing in their own country, led a miserable life among the woods, rocks, and mountains, with scarcely enough food to support life, and expecting every moment to be their last.
CHAPTER XVI
THE BRITONS OBTAINED THEIR FIRST VICTORY OVER THE ANGLES, UNDER THE COMMAND OF AMBROSIUS, A ROMAN
WHEN the victorious army, having destroyed and dispersed the natives, had returned home to their own settlements, the Britons began by degrees to take heart, and gather strength, sallying out of the lurking places where they had concealed themselves, and unanimously imploring the Divine assistance, that they might not utterly be destroyed. They had at that time for their leader, Ambrosius Aurelius, a modest man, who alone, by chance, of the Roman nation had survived the storm, in which his parents, who were of the royal race, had perished. Under him the Britons revived, and offering battle to the victors, by the help of God, came off victorious. From that day, sometimes the natives, and sometimes their enemies, prevailed, till the year of the siege of Baddesdownhill, when they made no small slaughter of those invaders, about forty-four years after their arrival in England. But of this hereafter.
CHAPTER XVII
HOW GERMANUS THE BISHOP, SAILING INTO BRITAIN WITH LUPUS, FIRST QUELLED THE TEMPEST OF THE SEA, AND AFTERWARDS THAT OF THE PELAGIANS, BY DIVINE POWER, [A.D. 429.]
SOME few years before their arrival, the Pelagian heresy brought over by Agricola, the son of Severianus, a Pelagian bishop, had sadly corrupted the faith of the Britons.6 But whereas they absolutely refused to embrace that perverse doctrine, so blasphemous against the grace of Christ, and were not able of themselves to confute its subtlety by force of argument, they thought of an excellent plan, which was to crave aid of the Gallican prelates in that spiritual war. Hereupon having gathered a great synod, they consulted together what persons should be sent thither, and by unanimous consent, choice was made of the apostolical priests, Germanus, bishop of Auxerre, and Lupus of Troyes, to go into Britain to confirm it in the faith. They readily complied with the request and commands of the holy Church, and putting to sea, sailed half way over from Gaul to Britain with a fair wind. There on a sudden they were obstructed by the malevolence of demons, who were jealous that such men should be sent to bring back the Britons to the faith. They raised storms, and darkened the sky with clouds. The sails could not bear the fury of the winds, the sailors' skill was forced to give way, the ship was sustained by prayer, not by strength, and as it happened, their spiritual commander and bishop, being spent with weariness, had fallen asleep. Then the tempest, as if the person that opposed it had given way, gathered strength, and the ship, overpowered by the waves, was ready to sink. Then the blessed Lupus and all the rest awakened their elder, that he might oppose the raging elements. He, showing himself the more resolute in proportion to the greatness of the danger, called upon Christ, and having, in the name of the Holy Trinity, sprinkled a little water, quelled the raging waves, admonished his companion, encouraged all, and all unanimously fell to prayer. The Deity heard their cry, the enemies were put to flight, a calm ensued, the winds veering about applied themselves to forward their voyage, and having soon traversed the ocean, they enjoyed the quiet of the wished for shore. A multitude flocking thither from all parts, received the priests, whose coming had been foretold by the predictions even of their adversaries. For the wicked spirits declared what they feared, and when the priests afterwards expelled them from the bodies they had taken possession of, they made known the nature of the tempest, and the dangers they had occasioned, and that they had been overcome by the merits and authority of the saints.
In the meantime, the apostolical priests filled the island of Britain with the fame of their preaching and virtues; and the word of God was by them daily administered, not only in the churches, but even in the streets and fields, so that the Catholics were everywhere confirmed, and those who had gone astray, corrected. Likewise the apostles, they had honour and authority through a good conscience, obedience to their doctrine through their sound learning, whilst the reward of virtue attended upon their numerous merits. Thus the generality of the people readily embraced their opinions; the authors of the erroneous doctrines kept themselves in the background, and, like evil spirits, grieved for the loss of the people that were rescued from them. At length, after mature deliberation they had the boldness to enter the lists, and appeared for public disputation, conspicuous for riches, glittering in apparel, and supported by the flatteries of many; choosing rather to hazard the combat, than to undergo the dishonour among the people of having been silenced, lest they should seem by saying nothing to condemn themselves. An immense multitude was there assembled with their wives and children. The people stood round as spectators and judges; but the parties present differed much in appearance; on the one side was Divine faith, on the other human presumption; on the one side piety, on the other pride; on the one side Pelagius on the other Christ. The holy priests, Germanus and Lupus, permitted their adversaries to speak first, who long took up the time, and filled the ears with empty words. Then the venerable prelates poured forth the torrent of their apostolical and evangelical eloquence. Their discourse was interspersed with scriptural sentences, and they supported their most weighty assertions by reading the written testimonies of famous writers. Vanity was convinced, and perfidiousness confuted; so, that at every objection made against them, not being able to reply, they confessed their errors. The people, who were judges, could scarcely refrain from violence, but signified their judgment by their acclamations.
CHAPTER XVIII
THE SAME HOLY MAN GAVE SIGHT TO THE BLIND DAUGHTER OF A TRIBUNE, AND THEN COMING TO ST. ALBAN'S, THERE RECEIVED SOME OF HIS RELICS AND LEFT OTHERS OF THE BLESSED APOSTLES, AND OTHER MARTYRS
AFTER this, a certain man, who had the quality of a tribune, came forward with his wife, and presented his blind daughter, ten years of age, for the priests to cure. they ordered her to be set before their adversaries, who, being convinced by guilt of conscience, joined their entreaties to those of the child's parents, and besought the priests that she might be cured. The priests, therefore, perceiving their adversaries to yield, made a short prayer, and then Germanus, full of the Holy Ghost, invoked the Trinity, and taking into his hands a casket with relics of saints, which hung about his neck, applied it to the girl's eyes, which were immediately delivered from darkness and filled with the light of truth. The parents rejoiced, and the people were astonished at the miracle; after which, the wicked opinions were so fully obliterated from the minds of all, that they ardently embraced the doctrine of the priests.
This damnable heresy being thus suppressed, and the authors thereof confuted, and all the people's hearts settled in the purity of the faith, the priests repaired to the tomb the martyr, St. Alban, to give thanks to God through him. There Germanus, having with him relics of all the Apostles, and of several martyrs, after offering up his prayers, commanded the tomb to be opened, that he might lay up therein some precious gifts; judging it convenient, that the limbs of saints brought together from several countries, as their equal merits had procured them admission into heaven, should he preserved in one tomb. These being honourably deposited, and laid together, he took up a parcel of dust from the place where the martyr's blood had been shed, to carry away with him, which dust having retained the blood, it appeared that the slaughter of the martyrs had communicated a redness to it, whilst the persecutor was struck pale. In consequence of these things, an innumerable multitude of people was that day converted to the Lord.
CHAPTER XIX
HOW THE SAME HOLY MAN, BEING DETAINED THERE BY AN INDISPOSITION, BY HIS PRAYERS QUENCHED A FIRE THAT HAD BROKEN OUT AMONG THE HOUSES, AND WAS HIMSELF CURED OF A DISTEMPER BY A VISION. [A.D. 429.]
AS they were returning from thence, Germanus fell and broke his leg, by the contrivance of the Devil, who did not know that, like Job, his merits would be enhanced by the affliction of his body. Whilst he was thus detained some time in the same place by illness, a fire broke out in a cottage neighbouring to that in which he was; and having burned down the other houses which were thatched with reed, was carried on by the wind to the dwelling in which he lay. The people all flocked to the prelate, entreating that they might lift him in their arms, and save him from the impending danger. He, however, rebuked them, and relying on faith, would not suffer himself to be removed. The multitude, in despair, ran to oppose the conflagration; however, for the greater manifestation of the Divine power, whatsoever the crowd endeavoured to save, was destroyed; but what he who was disabled and motionless occupied, the flame avoided, sparing the house that gave entertainment to the holy man, and raging about on every side of it; whilst the house in which he lay appeared untouched, amid the general conflagration. The multitude rejoiced at the miracle, and praised the superior power of God. An infinite number of the poorer sort watched day and night before the cottage; some to heal their souls, and some their bodies. It is impossible to relate what Christ wrought by his servant, what wonders the sick man performed: for whilst he would suffer no medicines to be applied to his distemper, he one night saw a person in garments as white as snow, standing by him, who reaching out his hand, seemed to raise him up, and ordered him to stand boldly upon his feet; from which time his pain ceased, and he was so perfectly restored, that when the day came on, he, without any hesitation, set forth upon his journey.
CHAPTER XX
HOW THE SAME BISHOPS PROCURED THE BRITONS ASSISTANCE FROM HEAVEN IN A BATTLE, AND THEN RETURNED HOME. [A.D. 429.]
IN the meantime, the Saxons and Picts, with their united forces, made war upon the Britons, who, being thus by fear and necessity compelled to take up arms, and thinking themselves unequal to their enemies, implored the assistance of the holy bishops; who, hastening to them as they had promised, inspired so much courage into these fearful people, that one would have thought they had been joined by a mighty army. Thus, by these holy apostolic men, Christ Himself commanded in their camp. The holy days of Lent were also at hand, and were rendered more religious by the presence of the priests, insomuch that the people being instructed by daily sermons, resorted in crowds to be baptized; for most of the army desired admission to the saving water; a church was prepared with boughs for the feast of the resurrection of our Lord, and so fitted up in that martial camp, as if it were in a city. The army advanced, still wet with the baptismal water; the faith of the people was strengthened and whereas human power had before been despaired of, the Divine assistance was now relied upon. The enemy received advice of the state of the army, and not questioning their success against an unarmed multitude, hastened forwards, but their approach was, by the scouts, made known to the Britons; the greater part of whose forces being just come from the font, after the celebration of Easter, and preparing to arm and carry on the war, Germanus declared he would be their leader. He picked out the most active, viewed the country round about, and observed, in the way by which the enemy was expected, a valley encompassed with hills. In that place he drew up his inexperienced troops, himself acting as their general. A multitude of fierce enemies appeared, whom as soon as those that lay in ambush saw a Pp roaching, Germanus, bearing in his hands the standard instructed his men all in a loud voice to repeat his words, and the enemy advancing securely, as thinking to take them by surprise, the priests three times cried, Hallelujah. A universal shout of the same word followed, and the hills resounding the echo on all sides, the enemy was struck with dread, fearing, that not only the neighbouring rocks, but even the very skies were falling upon them and such was their terror, that their feet were not swift enough to deliver them from it. They fled in disorder, casting away their arms, and well satisfied if, with their naked bodies, they could escape the danger; many of them, in their precipitate and hasty flight, were swallowed up by the river which they were passing. The Britons, without the loss of a man, beheld their vengeance complete, and became inactive spectators of their victory. The scattered spoils were gathered up, and the pious soldiers rejoiced in the success which heaven had granted them. The prelates thus triumphed over the enemy without bloodshed, and gained a victory by faith, without the aid of human force and, having settled the affairs of the Island, and restored tranquillity by the defeat, as well as of the invisible; as of the carnal enemies, prepared to return home. Their own merits, and the intercession of the holy martyr Alban, obtained them a safe passage, and the happy vessel restored them in peace to their rejoicing people.
CHAPTER XXI
THE PELAGIAN HERESY AGAIN REVIVING, GERMANUS, RETURNING INTO BRITAIN WITH SEVERUS, FIRST HEALED A LAME YOUTH, THEN HAVING CONDEMNED OR CONVERTED THE HERETICS, THEY RESTORED SPIRITUAL HEALTH TO THE PEOPLE OF GOD. [A.D. 447.]
NOT long after, advice was brought from the same island that certain persons were again attempting to set forth and spread abroad the Pelagian heresy. The holy Germanus was entreated by all the priests, that he would again defend the cause of God, which he had before asserted. He speedily complied with their request; and taking with him Severus, a man of singular sanctity who was disciple to the most holy father, Lupus, bishop of Troyes, and afterwards, as bishop of Treves, preached the word of God in the adjacent parts of Germany, put to sea, and was calmly wafted over into Britain.
In the meantime, the wicked spirits flying about the whole island, foretold by constraint that Germanus was coming, insomuch that one Elafius, a chief of that region, hastened to meet the holy men, without having received any certain news, carrying with him his son, who laboured under a weakness of his limbs in the very flower of his youth; for the nerves being withered, his leg was so contracted that the limb was useless, and he could not walk. All the country followed this Elafius. The priests arrived, and were met by the ignorant multitude, whom they blessed, and preached the word of God to them. They found the people constant in the faith as they had left them; and learning that but few had gone astray, they found out the authors, and condemned them. Then Elafius cast himself at the feet of the priests, presenting his son, whose distress was visible, and needed no words to express it. All were grieved, but especially the priests, who put up their prayers for him before the throne of mercy; and Germanus, causing the youth to sit down, gently passed his healing hand over the leg which was contracted; the limb recovered its strength and soundness by the power of his touch, the withered nerves were restored, and the youth was, in the presence of all the people delivered whole to his father. The multitude was amazed at the miracle, and the Catholic faith was firmly planted in the minds of all; after which, they were, in a sermon warned and exhorted to make amends for their errors. By the judgment of all, the spreaders of the heresy, who had been expelled the island, were brought before the priests, to be conveyed up into the continent, that the country might be rid of them, and they corrected of their errors. Thus the faith in those parts continued long after pure and untainted. All things being settled, he blessed prelates returned home as prosperously as they came.
But Germanus, after this, went to Ravenna to intercede for the tranquillity of the Armoricans, where, being very honourably received by Valentinian and his mother, Placidia, he departed to Christ; his body was conveyed to his own city with a splendid retinue, and numberless deeds of charity accompanied him to the grave. Not long after, Valentinian was murdered by the followers of Ætius, the Patrician; whom he had put to death, in the sixth year of the reign of Marcianus, and with him ended the empire of the West.
CHAPTER XXII
THE BRITONS, BEING FOR A TIME DELIVERED FROM FOREIGN INVASIONS, WASTED THEMSELVES BY CIVIL WARS, AND THEN GAVE THEMSELVES UP TO MORE HEINOUS CRIMES
IN the meantime, in Britain, there was some respite from foreign, but not from civil war. There still remained the ruins of cities destroyed by the enemy, and abandoned; and the natives, who had escaped the enemy, now fought against each other. However, the kings, priests, private men, and the nobility, still remembering the late calamities and slaughters, in some measure kept within bounds; but when these died, and another generation succeeded, which knew nothing of those times, and was only acquainted with the present peaceable state of things, all the bonds of sincerity and justice were so entirely broken, that there was not only no trace of them remaining, but few persons seemed to be aware that such virtues had ever existed. Among other most wicked actions, not to be expressed, which their own historian, Gildas, mournfully takes notice of, they added this that they never preached the faith to the Saxons, or English, who dwelt amongst them; however, the goodness of God did not forsake his people whom He foreknew, but sent to the aforesaid nation much more worthy preachers, to bring it to the faith.
Footnotes
[1] The Picts were an indigenous groups of people from the region in northern Britain, roughly corresponding with modern Scotland.
[2] This refers to Theodosius II (402-250), who ruled both the eastern and western halves of the Roman empire from his uncle Honorius' death in 423 until his own death in 450.
[3] Aetius was a military leader under the Western Roman emperor Valentinian III (425-455).
[4] Bede in this section and some of the following sections is paraphrasing the British historian Gildas, who wrote a long and rambling history of the murky period c. 400-550. Bede also paraphrases Gildas' argument that God sent the various barbarian peoples of northern Europe in order to punish the Britons for their sins.
[5] It's unclear what Bede's sources are for the figures of Hengist and Horsa, because he's the first known person to mention them as shadowy Germanic military leaders.
[6] As noted in the introduction above, Pelagius was a British bishop who was popular in Rome in the early 400s. One of his main teachings was that salvation could be attained through good works and righteousness. This pitted him against the African theological titan of the age, Augustine of Hippo, and divided clergy all over the Roman empire.
2) Conversion to Christianity: Practical Considerations (HE 1.25-27, 30-33) (return to top)
Response questions for this section:
1) How would you characterize the meeting between Ethelbert, king of Kent, and Augustine, the missionary sent by Pope Gregory I? What does this tell us about Bede's understanding of cultural encounters between different people?
2) 1.27 is a long section that scholars typically call the Liber responsionum, or the "Book of Responses" of Pope Gregory I to Augustine, his missionary. What types of questions does Augustine have, and why do you think this is? How would you characterize Gregory's responses?
CHAPTER XXV
AUGUSTINE, COMING INTO BRITAIN, FIRST PREACHED IN THE ISLE OF THANET TO KING ETHELBERT, AND HAVING OBTAINED LICENCE, ENTERED THE KINGDOM OF KENT, IN ORDER TO PREACH THEREIN. [A.D. 597.]
AUGUSTINE, thus strengthened by the confirmation of the blessed Father Gregory, returned to the work of the word of God, with the servants of Christ, and arrived in Britain. The powerful Ethelbert1 was at that time king of Kent; he had extended his dominions as far as the great river Humber, by which the Southern Saxons are divided from the Northern. On the east of Kent is the large Isle of Thanet containing according to the English way of reckoning, 600 families, divided from the other land by the river Wantsum, which is about three furlongs over, and fordable only in two places, for both ends of it run into the sea. In this island landed the servant of our Lord, Augustine, and his companions, being, as is reported, nearly forty men. They had, by order of the blessed Pope Gregory, taken interpreters of the nation of the Franks, and sending to Ethelbert, signified that they were come from Rome, and brought a joyful message, which most undoubtedly assured to all that took advantage of it everlasting joys in heaven and a kingdom that would never end with the living and true God. The king having heard this, ordered them to stay in that island where they had landed, and that they should be furnished with all necessaries, till he should consider what to do with them. For he had before heard of the Christian religion, having a Christian wife of the royal family of the Franks, called Bertha; whom he had received from her parents, upon condition that she should be permitted to practice her religion with the Bishop Luidhard, who was sent with her to preserve her faith.2 Some days after, the king came into the island, and sitting in the open air, ordered Augustine and his companions to be brought into his presence. For he had taken precaution that they should not come to him in any house, lest, according to an ancient superstition, if they practiced any magical arts, they might impose upon him, and so get the better of him. But they came furnished with Divine, not with magic virtue, bearing a silver cross for their banner, and the image of our Lord and Saviour painted on a board; and singing the litany, they offered up their prayers to the Lord for the eternal salvation both of themselves and of those to whom they were come. When he had sat down, pursuant to the king's commands, and preached to him and his attendants there present, the word of life, the king answered thus: "Your words and promises are very fair, but as they are new to us, and of uncertain import, I cannot approve of them so far as to forsake that which I have so long followed with the whole English nation. But because you are come from far into my kingdom, and, as I conceive, are desirous to impart to us those things which you believe to be true, and most beneficial, we will not molest you, but give you favourable entertainment, and take care to supply you with your necessary sustenance; nor do we forbid you to preach and gain as many as you can to your religion." Accordingly he permitted them to reside in the city of Canterbury, which was the metropolis of all his dominions, and, pursuant to his promise, besides allowing them sustenance, did not refuse them liberty to preach. It is reported that, as they drew near to the city, after their manner, with the holy cross, and the image of our sovereign Lord and King, Jesus Christ, they, in concert, sung this litany: "We beseech Thee, O Lord, in all Thy mercy, that thy anger and wrath be turned away from this city, and from the holy house, because we have sinned. Hallelujah."
CHAPTER XXVI
ST. AUGUSTINE IN KENT FOLLOWED THE DOCTRINE AND MANNER OF LIVING OF THE PRIMITIVE CHURCH, AND SETTLED HIS EPISCOPAL SEE IN THE ROYAL CITY. [A.D. 597.]
As soon as they entered the dwellingplace assigned them they began to imitate the course of life practiced in the primitive church; applying themselves to frequent prayer, watching and fasting; preaching the word of life to as many as they could; despising all worldly things, as not belonging to them; receiving only their necessary food from those they taught; living themselves in all respects conformably to what they prescribed to others, and being always disposed to suffer any adversity, and even to die for that truth which they preached. In short, several believed and were baptized, admiring the simplicity of their innocent life, and the sweetness of their heavenly doctrine. There was on the east side of the city a church dedicated to the honour of St. Martin, built whilst the Romans were still in the island, wherein the queen, who, as has been said before, was a Christian, used to pray. In this they first began to meet, to sing, to pray, to say mass, to preach, and to baptize, till the king, being converted to the faith, allowed them to preach openly, and build or repair churches in all places.
When he, among the rest, induced by the unspotted life of these holy men, and their delightful promises, which, by many miracles, they proved to be most certain, believed and was baptized, greater numbers began daily to flock together to hear the word, and, forsaking their heathen rites, to associate themselves, by believing, to the unity of the church of Christ. Their conversion the king so far encouraged, as that he compelled none to embrace Christianity, but only showed more affection to the believers, as to his fellowcitizens in the heavenly kingdom. for he had learned from his instructors and leaders to salvation, that the service of Christ ought to be voluntary, not by compulsion. Nor was it long before he gave his preachers a settled residence in his metropolis of Canterbury, with such possessions of different kinds as were necessary for their subsistence.
CHAPTER XXVII
IN the meantime, Augustine, the man of God, repaired to Arles, and, pursuant to the orders received from the holy Father Gregory, was ordained archbishop of the English nation, by Ætherius, archbishop of that city. Then returning into Britain, he sent Laurentius the priest, and Peter the monk, to Rome, to acquaint Pope Gregory, that the nation of the English had received the faith of Christ, and that he was himself made their bishop. At the same time, he desired his solution of some doubts that occurred to him. He soon received proper answers to his questions which we have also thought fit to insert in this, our history .
The First Question of Augustine, Bishop of the Church of Canterbury. Concerning bishops, how they are to behave themselves towards their clergy? or into how many portions the things given by the faithful to the altar are to he divided? and how the bishop is to act in the church?
Gregory, Pope of the City of Rome, answers. Holy Writ, which no doubt you are well versed in, testifies, and particularly St. Paul's Epistle to Timothy, wherein he endeavours to instruct him how he should behave himself in the house of God; but it is the custom of the apostolic see to prescribe rules to bishops newly ordained, that all emoluments which accrue, are to he divided into four portions; one for the bishop and his family, because of hospitality and entertainments; another for the clergy; a third for the poor; and the fourth for the repair of churches. But in regard that you, my brother, being brought up under monastic rules, are not to live apart from your clergy in the English church, which, by God's assistance, has been lately brought to the faith; you are to follow that course of life which our forefathers did in the time of the primitive church, when none of them said anything that he possessed was his own, but all things were in common among them.
[. . .]
Pope Gregory answers. You know, my brother, the custom of the Roman church in which you remember you were bred up. But it pleases me, that if you have found anything, either in the Roman, or the Gallican, or any other church, which may be more acceptable to Almighty God, you carefully make choice of the same, and sedulously teach the church of the English, which as yet is new ln the faith, whatsoever you can gather from the several churches. For things are not to be loved for the sake of places, but places for the sake of good things. Choose, therefore, from every church those things that are pious, religious, and upright, and when you have, as it were, made them up into one body, let the minds of the English be accustomed thereto.
Augustine's Third Question. I beseech you to inform me, what punishment must be inflicted, if any one shall take anything by stealth from the church?
Gregory answers. You may judge, my brother, by the person of the thief, in what manner he is to be corrected. For there are some, who, having substance, commit theft; and there are others, who transgress in this point through want. Wherefore it is requisite, that some be punished in their purses, others with stripes; some with more severity, and some more mildly. And when the severity is more, it is to proceed from charity, not from passion; because this is done to him who is corrected, that he may not be delivered up to hellfire. For it behooves us to maintain discipline among the faithful, as good parents do with their carnal children, whom they punish with stripes for their faults, and yet design to make those their heirs whom they chastise; and they preserve what they possess for those whom they seem in anger to persecute. This charity is, therefore, to be kept in mind, and it dictates the measure of the punishment, so that the mind may do nothing beyond the rule of reason. You may add, that they are to restore those things which they have stolen from the church. But, God forbid, that the church should make profit from those earthly things which it seems to lose, or seek gain out of such vanities.
Augustine's Fourth Question. Whether two brothers may marry two sisters, which are of a family far removed from them?
Gregory answers. This may lawfully be done; for nothing is found in holy writ that seems to contradict it.
Augustine's Fifth Question. Of what degree may the faithful marry with their kindred? And whether it is lawful for men to marry their stepmother and relations?
Gregory answers. A certain worldly law in the Roman commonwealth allows, that the son and daughter of a brother and sister, or of two brothers, or two sisters, may be joined in matrimony; but we have found, by experience, that no offspring can come of such wedlock; and the Divine Law forbids a man to "uncover the nakedness of his kindred." Hence of necessity it must be the third or fourth generation of the faithful, that can be lawfully joined in matrimony; for the second, which we have mentioned, must altogether abstain from one another. To marry with one's stepmother is a heinous crime, because is written in the Law, "Thou shalt not uncover the nakedness of thy father": now the son, indeed, cannot uncover his father's nakedness; but in regard that it is written, "They shall be two in one flesh," he that presumes to uncover the nakedness of his stepmother, who was one flesh with his father, certainly uncovers the nakedness of his father. It is also prohibited to marry with a sister in law, because by the former union she is become the brother's flesh. For which thing also John the Baptist was beheaded, and ended his life in holy martyrdom. For, though he was not ordered to deny Christ, and indeed was killed for confessing Christ, yet in regard that the same Jesus Christ, our Lord, said, "I am the Truth," because John was killed for the truth, be also shed his blood for Christ.
But forasmuch as there are many of the English, who whilst they were still in infidelity, are said to have been joined in this execrable matrimony, when they come to the faith they are to be admonished to abstain, and be made to know that this is a grievous sin. Let them fear the dreadful judgment of God, lest, for the gratification of their carnal appetites, they incur the torments of eternal punishment. Yet they are not on this account to be deprived of the communion of the body and blood of Christ, lest they seem to be punished for those things which they did through ignorance before they had received baptism. For at this time the Holy Church chastises some things through zeal, and tolerates some through meekness, and connives at some things through discretion, that so she may often, by this forbearance and connivance, suppress the evil which she disapproves. But all that come to the Faith are to be admonished not to do such things. And if any shall be guilty of them, they are to be excluded from the communion of the body and blood of Christ. For as the offence is, in some measure, to be tolerated in those who did it through ignorance, so it is to be strenuously prosecuted in those who do not fear to sin knowingly.
Augustine's Sixth Question. Whether a bishop may be ordained without other bishops being present, in case there be so great a distance between them, that they cannot easily come together?
Gregory answers. As for the church of England, in which you are as yet the only bishop, you can no otherwise ordain a bishop than in the absence of other bishops; unless some bishops should come over from Gaul, that they may be present as witnesses to you in ordaining a bishop. But we would have you, my brother, to ordain bishops in such a manner, that the said bishops may not be far asunder, that when a new bishop is to he ordained, there be no difficulty, but that other bishops, and pastors also, whose presence is necessary, may easily come together. Thus, when, by the help of God, bishops shall be so constituted in places everywhere near to one another, no ordination of a bishop is to be performed without assembling three or four bishops.
[. . .]
Augustine's Seventh Question. How are we to deal with the bishops of France and Britain?
Gregory answers. We give you no authority over the bishops of France, because the bishop of Aries received the pall5 in ancient times from my predecessor, and we are not to deprive him of the authority he has received.
[. . .]
Augustine's Eighth Question. Whether a woman with child ought to be baptized? Or how long after she has brought forth, may she come into the church? As also, after how many days the infant born may be baptized, lest he be prevented by death? Or how long after her husband may have carnal knowledge of her? Or whether it is lawful for her to come into the church when she has her courses? Or to receive the holy sacrament of communion? Or whether a man, under certain circumstances, may come into the church before he has washed with water? Or approach to receive the mystery of the holy communion? All which things are requisite to be known by the rude nation of the English.
Gregory answers. I do not doubt but that these questions have been put to you, my brother, and I think I have already answered you therein. But I believe you would wish the opinion which you yourself might give to be confirmed by mine also. Why should not a woman with child be baptized, since the fruitfulness of the flesh is no difference in the eyes of Almighty God? For when our first parents sinned in Paradise, they forfeited the immortality which they had received, by the just judgment of God. Because, therefore, Almighty God would not for their fault wholly destroy the human race, He both deprived man of immortality for his sin, and, at the same time, of his great goodness, reserved to him the power of propagating his race after him. On what account then can that which is preserved to the human race, by the free gift of Almighty God, be excluded from the privilege of baptism? For it is very foolish to imagine that the gift of grace opposes that mystery in which all sin is blotted out. When a woman is delivered, after how many days she may come into the church, you have been informed by reading the Old Testament, that she is to abstain for a male child thirty-three days, and sixty-six for a female. Now you must know that this is to be taken in a mystery; for if she enters the church the very hour that she is delivered, to return thanks, she is not guilty of any sin; because the pleasure of the flesh is in fault, and not the pain; but the pleasure is in the copulation of the flesh, whereas there is pain in bringing forth the child. Wherefore it is said to the first mother of all, "In sorrow shalt thou bring forth children." If, therefore, we forbid a woman that has brought forth [a child], to enter the church, we make a crime of her very punishment.
[. . .]
Her husband is not to approach her, till the infant born be weaned. A bad custom is sprung up in the behaviour of married people, that is, that women disdain to suckle the children which they bring forth, and give them to other women to suckle; which seems to have been invented on no other account but incontinency; because, as they will not be continent, they will not suckle the children which they bear. Those women, therefore, who, from bad custom, give their children to others to bring up, must not approach their husbands till the time of purification is past.
[. . .]
She must not, therefore, be forbidden to receive the mystery of the holy communion during those days. But if any one out of profound respect does not presume to do it, she is to be commended; yet if she receives it, she is not to be judged. For it is the part of noble minds in some manner to acknowledge their faults, even where there is no offence; because very often that is done without a fault, which, nevertheless, proceeded from a fault. Therefore, when we are hungry, it is no crime to eat; yet our being hungry proceeds from the sin of the first man. The monthly courses are no crime in women; because they naturally happen; however, because our nature itself is so depraved, that it appears to be so without the concurrence of the will, the fault proceeds from sin, and thereby human nature may herself know what she is become by judgment. And let man, who wilfully committed the offence, bear the guilt of that offence. And, therefore, let women consider with themselves, and if they do not presume, during their monthly courses, to approach the sacrament of the body and blood of our Lord, they are to be commended for their praiseworthy consideration; but when they are carried away with love of the same mystery to receive it out of the usual custom of religious life, they are not to be restrained, as we said before.
[. . .]
A man who has approached his own wife is not to enter the church unless washed with water, nor is he to enter immediately although washed. The Law prescribed to the ancient people, that a man in such cases should be washed with water, and not enter into the church before the setting of the sun. Which, nevertheless, may be understood spiritually, because a man acts so when the mind is led by the imagination to unlawful concupiscence; for unless the fire of concupiscence be first driven from his mind, he is not to think himself worthy of the congregation of the brethren, whilst he thus indulges an unlawful passion. For though several nations have different opinions concerning this affair, and seem to observe different rules, it was always the custom of the Romans, from ancient times, for such an one to be cleansed by washing, and for some time respectfully to forbear entering the church. Nor do we, in so saying, assign matrimony to be a fault; but forasmuch as lawful intercourse cannot be had without the pleasure of the flesh, it is proper to forbear entering the holy place, because the pleasure itself cannot be without a fault.
[. . .]
It is seriously to be considered, that when God was to speak to the people on Mount Sinai, He first commanded them to abstain from women. And if so much cleanness of body was there required, where God spoke to the people by the means of a subject creature, that those who were to hear the words of God should not do so; how much more ought women, who receive the body of Almighty God, to preserve themselves in cleanness of flesh, lest they be burdened with the very greatness of that unutterable mystery? For this reason, it was said to David, concerning his men, by the priest, that if they were clean in this particular, they should receive the shewbread, which they would not have received at all, had not David first declared them to be clean. Then the man, who, afterwards, has been washed with water, is also capable of receiving the mystery of the holy communion, when it is lawful for him, according to what has been before declared, to enter the church.
Augustine's Ninth Question. - Whether after an illusion such as happens in a dream, any man may receive the body of our Lord, or if he be a priest, celebrate the Divine mysteries?
Gregory answers. The Testament of the Old Law, as has been said already in the article above, calls such a man polluted, and allows him not to enter into the church till the evening after being washed with water. Which, nevertheless, spiritual people, taking in another sense, will understand in the same manner as above; because he is imposed upon as it were in a dream, who, being tempted with filthiness, is defiled by real representations in thought, and he is to be washed with water, that he may cleanse away the sins of thought with tears; and unless the fire of temptation depart before, may know himself to be guilty as it were until the evening. But discretion is very necessary in that illusion, that one may seriously consider what causes it to happen in the mind of the person sleeping; for sometimes it proceeds from excess of eating or drinking; sometimes from the superfluity or infirmity of nature, and sometimes from the thoughts. And when it happens, either through superfluity or infirmity of nature, such an illusion is not to be feared, because it is rather to be lamented, that the mind of the person, who knew nothing of it, suffers the same, than that he occasioned it. But when the appetite of gluttony commits excess in food, and thereupon the receptacles of the humours are oppressed, the mind from thence contracts some guilt; yet not so much as to obstruct the receiving of the holy mystery, or celebrating mass, when a holy day requires it, or necessity obliges the sacrament to be administered, because there is no other priest in the place; for if there be others who can perform the ministry, the illusion proceeding from overeating is not to exclude a man from receiving the sacred mystery; but I am of opinion he ought humbly to abstain from offering the sacrifice of the mystery; but not from receiving it, unless the mind of the person sleeping has been filled with some foul imagination. For there are some, who for the most part so suffer the illusion, that their mind, even during the sleep of the body, is not defiled with filthy thoughts. In which case, one thing is evident, that the mind is guilty even in its own judgment; for though it does not remember to have seen any thing whilst the body was sleeping, yet it calls to mind that when waking it fell into bodily gluttony. But if the sleeping illusion proceeds from evil thoughts when waking, then the guilt is manifest to the mind; for the man perceives from whence that filth sprung, because what he had knowingly thought of, that he afterwards unwittingly revealed. But it is to be considered, whether that thought was no more than a suggestion, or proceeded to enjoyment, or, which is still more criminal, consented to sin. For all sin is fulfilled in three ways: by suggestion, by delight, and by consent. Suggestion is occasioned by the Devil, delight is from the flesh, and consent from the mind. For the serpent suggested the first offence, and Eve, as flesh; was delighted with it, but Adam consented, as the spirit, or mind. And much discretion is requisite for the mind to sit as judge between suggestion and delight, and between delight and consent.
[. . .]
CHAPTER XXX
A COPY OF THE LETTER WHICH POPE GREGORY SENT TO THE ABBOT MELLITUS, THEN GOING INTO BRITAIN. [A.D. 601.]
THE aforesaid messengers being departed, the holy father, Gregory, sent after them letters worthy to be preserved in memory, wherein he plainly shows what care he took of the salvation of our nation. The letter was as follows -
"To his most beloved son, the Abbot Mellitus; Gregory, the servant of the servants of God. We have been much concerned, since the departure of our congregation that is with you, because we have received no account of the success of your journey. When, therefore, Almighty God shall bring you to the most reverend Bishop Augustine, our brother, tell him what I have, upon mature deliberation on the affair of the English, determined upon, viz., that the temples of the idols in that nation ought not to be destroyed; but let the idols that are in them be destroyed; let holy water be made and sprinkled in the said temples, let altars be erected, and relics placed. For if those temples are well built, it is requisite that they be converted from the worship of devils to the service of the true God; that the nation, seeing that their temples are not destroyed, may remove error from their hearts, and knowing and adoring the true God, may the more familiarly resort to the places to which they have been accustomed. And because they have been used to slaughter many oxen in the sacrifices to devils, some solemnity must be exchanged for them on this account, as that on the day of the dedication, or the nativities of the holy martyrs, whose relics are there deposited, they may build themselves huts of the boughs of trees, about those churches which have been turned to that use from temples, and celebrate the solemnity with religious feasting, and no more offer beasts to the Devil, but kill cattle to the praise of God in their eating, and return thanks to the Giver of all things for their sustenance; to the end that, whilst some gratifications are outwardly permitted them, they may the more easily consent to the inward consolations of the grace of God. For there is no doubt that it is impossible to efface everything at once from their obdurate minds; because he who endeavours to ascend to the highest place, rises by degrees or steps, and not by leaps. Thus the Lord made Himself known to the people of Israel in Egypt; and yet He allowed them the use of the sacrifices which they were wont to offer to the Devil, in his own worship; so as to command them in his sacrifice to kill beasts, to the end that, changing their hearts, they might lay aside one part of the sacrifice, whilst they retained another; that whilst they offered the same beasts which they were wont to offer, they should offer them to God, and not to idols; and thus they would no longer be the same sacrifices. This it behooves your affection to communicate to our aforesaid brother, that he, being there present, may consider how he is to order all things. God preserve you in safety, most beloved son.
Given the 17th of June, in the nineteenth year of the reign of our lord, the most pious emperor, Mauritius Tiberius, the eighteenth year after the consulship of our said lord. The fourth indiction."
CHAPTER XXXI
POPE GREGORY, BY LETTER, EXHORTS AUGUSTINE NOT TO GLORY IN HIS MIRACLES. [A.D. 601.]
AT which time he also sent Augustine a letter concerning the miracles that he had heard had been wrought by him; wherein he admonishes him not to incur the danger of being puffed up by the number of them. The letter was in these words -
"I know, most loving brother, that Almighty God, by means of your affection, shows great miracles in the nation which He has chosen. Wherefore it is necessary that you rejoice with fear, and tremble whilst you rejoice, on account of the same heavenly gift; viz., that you may rejoice because the souls of the English are by outward miracles drawn to inward grace; but that you fear, lest, amidst the wonders that are wrought, the weak mind may be puffed up in its own presumption, and as it is externally raised to honour, it may thence inwardly fall by vainglory. For we must call to mind, that when the disciples returned with joy after preaching, and said to their heavenly Master, 'Lord, in thy name, even the devils are subject to us;' they were presently told, 'Do not rejqice on this account, but rather rejoice for that your names are written in heaven.' For they placed their thoughts on private and temporal joy , when they rejoiced in miracles; but they are recalled from the private to the public, and from the temporal to the eternal joy, when it is said to them, 'Rejoice for this, because your names are written in heaven.' For all the elect do not work miracles, and yet the names of all are written in heaven. For these who are disciples of the truth ought not to rejoice, save for that good thing which all men enjoy as well as they, and of which their enjoyment shall be without end.
It remains, therefore, most dear brother, that amidst those things, which through the working of our Lord, you outwardly perform, you always inwardly strictly judge yourself, and clearly understand both what you are yourself, and how much grace is in that same nation, for the conversion of which you have also received the gift of working miracles. And if you remember that you have at any time offended our Creator, either by word or deed, that you always call it to mind, to the end that the remembrance of your guilt may crush the vanity which rises in your heart. And whatsoever you shall receive, or have received, in relation to working miracles, that you consider the same, not as conferred on you, but on those for whose salvation it has been given you."
CHAPTER XXXII
POPE GREGORY SENDS LETTERS AND PRESENTS TO KING ETHELBERT
THE same holy Pope Gregory, at the same time, sent a letter to King Ethelbert, with many presents of several sorts; being desirous to glorify the king with temporal honours, at the same time that he rejoiced that through his labour and zeal he had attained the knowledge of the heavenly glory. The copy of the said letter is as follows -
"To the most glorious Lord, and his most excellent son, Ethelbert, king of the English, Bishop Gregory. Almighty God advances all good men to the government of nations, that He may by their means bestow the gifts of his mercy on those over whom they are placed. This we know to have been done in the English nation, over whom your glory was therefore placed, that by means of the goods which are granted to you, heavenly benefits might also be conferred on the nation that is subject to you. Therefore, my illustrious son, do you carefully preserve the grace which you have received from the Divine goodness, and hasten to promote the Christian faith, which you have embraced, among the people under your subjection; multiply the zeal of your uprightness in their conversion; suppress the worship of idols; overthrow the structures of the temples; edify the manners of your subjects by much cleanness of life, exhorting, terrifying, soothing, correcting, and giving examples of good works, that you may find Him your rewarder in heaven, whose name and knowledge you shall spread abroad upon earth. For He also will render the fame of your honour more glorious to posterity, whose honour you seek and maintain among the nations.
For even so Constantine,6 our most pious emperor, recovering the Roman commonwealth from the perverse worship of idols, subjected the same with himself to our Almighty God and Lord Jesus Christ, and was himself, with the people under his subjection, entirely converted to Him. Whence it followed, that his praises transcended the fame of former princes; and he as much excelled his predecessors in renown as he did in good works. Now, therefore, let your glory hasten to infuse into the kings and people that are subject to you, the knowledge of one God, Father, Son, and Holy Ghost; that you may both surpass the ancient kings of your nation in praise and merit, and become by so much the more secure against your own sins before the dreadful judgment of Almighty God, as you shall wipe away the sins of others in your subjects.
Willingly hear, devoutly perform, and studiously retain in your memory, whatsoever you shall be advised by our most reverend brother, Bishop Augustine, who is instructed in the monastical rule, full of the knowledge of the holy Scripture, and, by the help of God, endued with good works; for if you give ear to him in what he speaks for Almighty God, the same Almighty God will the sooner hear him praying for you. But if (which God avert!) you slight his words, how shall Almighty God hear him in your behalf, when you neglect to hear him for God? Unite yourself, therefore, to him with all your mind, in the fervour of faith, and further his endeavours, through the assistance of that virtue which the Divinity affords you, that He may make you partaker of his kingdom, whose faith you cause to be received and maintained in your own.
Besides, we would have your glory know, we find in the holy Scripture, from the words of the Almighty Lord, that the end of this present world, and the kingdom of the saints, is about to come, which will never terminate. But as the same end of the world approaches, many things are at hand which were not before, viz. changes of air, and terrors from heaven, and tempests out of the order of the seasons, wars, famines, plagues, earthquakes in several places; which things will not, nevertheless, happen in our days, but will all follow after our days. If you, therefore, find any of these things to happen in your country, let not your mind be in any way disturbed; for these signs of the end of the world are sent before, for this reason, that we may be solicitous for our souls, suspicious of the hour of death, and may be found prepared with good works to meet our Judge. Thus much, my illustrious son, I have said in few words, to the end that when the Christian faith shall increase in your kingdom, our discourse to you may also be more copious, and we may be pleased to say the more, in proportion as joy for the conversion of your nation is multiplied in our mind.
I have sent you some small presents, which will not appear small, when received by you with the blessing of the holy apostle, Peter. May Almighty God, therefore, perfect in you his grace which He has begun, and prolong your life here through a course of many years, and after a time receive you into the congregation of the heavenly country. May heavenly grace preserve your excellency in safety.
Given the 22nd day of June, in the nineteenth year of the reign of the most pious emperor, Mauritius Tiberius, in the eighteenth year after his consulship. Fourth indiction."
CHAPTER XXXIII
AUGUSTINE REPAIRS THE CHURCH OF OUR SAVIOUR, AND BUILDS THE MONASTERY OF ST. PETER THE APOSTLE; PETER THE FIRST ABBOT OF THE SAME. [A.D. 602.]
AUGUSTINE having his episcopal see granted him in the royal city, as has been said, and being supported by the king, recovered therein a church, which he was informed had been built by the ancient Roman Christians, and consecrated it in the name our holy Saviour, God and Lord, Jesus Christ, and there established a residence for himself and his successors. He also built a monastery not far from the city to the eastward, in which, by his advice, Ethelbert erected from the foundation the church of the blessed apostles, Peter and Paul, and enriched it with several donations; wherein the bodies of the same Angustine, and of all the bishops of Canterbury, and of the kings of Kent, might be buried. However, Augustine himself did not consecrate that church, but Laurentius, his successor.
The first abbot of that monastery was the priest Peter, who, being sent ambassador into France, was drowned in a bay of the sea, which is called Amfleat, and privately buried by the inhabitants of the place; but Almighty God, to show how deserving a man he was, caused a light to be seen over his grave every night; till the neighbours who saw it, perceiving that he had been a holy man that was buried there, inquiring who, and from whence he was, carried away the body, and interred it in the church, in the city of Boulogne, with the honour due to so great a person.
Footnotes
[1] Ethelbert (or Æthelberht) was king of Kent in southeastern Britain from 590-616.
[2] Bertha was the daughter of the Merovingian king Charibert I (561-567). (The Merovingians were a political dynasty in Francia, a barbarian-Christian kingdom established in what had been the Roman province of Gaul, or modern-day France.)
[3] This long chapter (1.27) is commonly referred to as the Liber responsionum, or "Book of Responses." It probably comes from a correspondence between Augustine the missionary and Gregory the pope, who gives (sometimes exasperated) replies to Augustine's very specific questions.
[4] "Gallic church" would be a better phrase here, since Bede is referring to the church of Gaul in western Europe (where France currently is situated).
[5] "Pall" refers to the pallium, a strip of white wool worn by popes and bishops when they oversee the litrugy, or script, of worship services. It's a symbol of their authority as shepherds of the faithful.
[6] As noted above, Constantine was the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity in the early 300s, and he fostered the religion's growth in the empire through his support of its leadership and the building of churches. The idea that a sitting pope would invoke this example to the recently-converted Ethelbert clearly pleases Bede.
3. Conversion and Royal Policy: A Case Study of King Edwin of Northumbria (HE 2.2-14) (return to top)
Response questions for this section:
1) Like the previous section, these chapters contain copies of letters between popes and monarchs. What is the nature of these letters? What advice do they offer, and why? What does this tell us about the practical considerations of conversion?
2) Chapter XIII details a meeting of King Edwin's council in which he seeks their advice on his own religious choices. What arguments is he presented with, and what do you think Bede is attempting to communicate about the ideas of mortality and eternity?
CHAPTER IX
THE REIGN OF KING EDWIN, AND HOW PAULINUS, COMING TO PREACH THE GOSPEL, FIRST CONVERTED HIS DAUGHTER AND OTHERS TO THE FAITH OF CHRIST. [A.D. 625.]
AT this time the nation of the Northumbrians, that is, the nation of the Angles that live on the north side of the river Humber, with their king, Edwin,1 received the faith . . . This Edwin, as a reward of his receiving the faith, and as an earnest of his share in the heavenly kingdom, received an increase of that which he enjoyed on earth, for he reduced under his dominion all the borders of Britain that were provinces either of the aforesaid nation, or of the Britons, a thing which no British king had ever done before; and he in like manner subjected to the English the Mevanian islands, as has been said above. The first whereof, which is to the southward, is the largest in extent, and most fruitful, containing nine hundred and sixty families, according to the English computation; the other above three hundred.
The occasion of this nation's embracing the faith was, their aforesaid king, being allied to the kings of Kent, having taken to wife Ethelberga, otherwise called Tate, daughter to King Ethelbert. He having by his ambassadors asked her in marriage of her brother Eadbald, who then reigned in Kent, was answered, "That it was not lawful to marry a Christian virgin to a pagan husband, lest the faith and the mysteries of the heavenly King should be profaned by her cohabiting with a king that was altogether a stranger to the worship of the true God."2 This answer being brought to Edwin by his messengers, he promised in no manner to act in opposition to the Christian faith, which the virgin professed; but would give leave to her, and all that went with her, men or women, priests or ministers, to follow their faith and worship after the custom of the Christians. Nor did he deny, but that he would embrace the same religion, if, being examined by wise persons, it should be found more holy and more worthy of God.
Hereupon the virgin was promised, and sent to Edwin, and pursuant to what had been agreed on, Paulinus, a man beloved of God, was ordained bishop, to go with her, and by daily exhortations, and celebrating the heavenly mysteries, to confirm her and her company, lest they should be corrupted by the company of the pagans. Paulinus was ordained bishop by the Archbishop Justus, on the 21st day of July, in the year of our Lord 625, and so he came to King Edwin with the aforesaid virgin as a companion of their union in the flesh. But his mind was wholly bent upon reducing the nation to which he was sent to the knowledge of truth; according to the words of the apostle, "To espouse her to one husband, that he might present her as a chaste virgin to Christ." Being come into that province, he laboured much, not only to retain those that went with him, by the help of God, that they should not revolt from the faith, but, if he could, to convert some of the pagans to a state of grace by his preaching. But, as the apostle says, though he laboured long in the word, "The god of this world blinded the minds of them that believed not, lest the light of the glorious Gospel of Christ should shine unto them."
The next year there came into the province a certain assassin, called Eumer, sent by the king of the West-Saxons, whose name was Cuichelm, in hopes at once to deprive King Edwin of his kingdom and his life. He had a two-edged dagger, dipped in poison, to the end, that if the wound were not sufficient to kill the king, it might be performed by the venom. He came to the king on the first day of Easter, at the river Derwent, where then stood the regal city, and being admitted as if to deliver a message from his master, whilst he was in an artful manner delivering his pretended embassy, he started on a sudden, and drawing the dagger from under his garment, assaulted the king; which Lilla, the king's beloved minister, observing, having no buckler at hand to secure the king from death, interposed his own body to receive the stroke; but the wretch struck so home, that he wounded the king through the knight's body. Being then attacked on all sides with swords, he in that confusion also slew another soldier, whose name was Forthhere.
On that same holy night of Easter Sunday, the queen had brought forth to the king a daughter, called Eanfled. The king, in the presence of Bishop Paulinus, gave thanks to his gods for the birth of his daughter; and the bishop, on the other hand, returned thanks to Christ, and endeavoured to persuade the king, that by his prayers to Him he had obtained that the queen should bring forth the child in safety, and without much pain. The king, delighted with his words, promised, that in case God would grant him life and victory over the king by whom the assassin had been sent, he would cast off his idols, and serve Christ; and as a pledge that he would perform his promise, he delivered up that same daughter to Paulinus, to be consecrated to Christ. She was the first baptized of the nation of the Northunibrians, on Whitsunday, with twelve others of her family. At that time, the king, being recovered of the wound which he had received, marched with his army against the nation of the West-Saxons; and having begun the war, either slew or subdued all those that he had been informed had conspired to murder him. Returning thus victorious unto his own country, he would not immediately and unadvisedly embrace the mysteries of the Christian faith, though he no longer worshipped idols, ever since he made the promise that he would serve Christ; but thought fit first at leisure to be instructed, by the venerable Paulinus, in the knowledge of faith, and to confer with such as he knew to be the wisest of his prime men, to advise what they thought was fittest to be done in that case. And being a man of extraordinary sagacity, he often sat alone by himself a long time, silent as to his tongue, but deliberating in his heart how he should proceed, and which religion he should adhere to.
CHAPTER X
POPE BONIFACE, BY LETTER, EXHORTS THE SAME KING TO EMBRACE THE FAITH. [A.D. 625.]
AT this time he received letters from Pope Boniface exhorting him to embrace the faith, which were as follows-
COPY OF THE LETTER OF THE HOLY AND APOSTOLIC POPE OF THE CHURCH OF ROME, BONIFACE, TO THE GLORIOUS EDWIN, KING OF THE ENGLISH.
"To the illustrious Edwin, king of the English, Bishop Boniface, the servant of the servants of God. Although the power of the Supreme Deity cannot be expressed by human speech, as consisting in its own greatness, and in invisible and unsearchable eternity, so that no sharpness of wit can comprehend or express it; yet in regard that the goodness of God, to give some notion of itself, having opened the doors of the heart, has mercifully, by secret inspiration, infused into the minds of men such things as He is willing shall be declared concerning Himself, we have thought fit to extend our priestly care to make known to you the fulness of the Christian faith; to the end that, informing you of the Gospel of Christ, which our Saviour commanded should be preached to all nations, they might offer to you the cup of life and salvation.
Thus the goodness of the Supreme Majesty, which, by the word of his command, made and created all things, the heaven, the earth, the sea, and all that is in them, disposing the order by which they should subsist, hath, with the counsel of his co-eternal Word, and the unity of the Holy Spirit, formed man after his own likeness, out of the slime of the earth; and granted him such super-eminent prerogative, as to place him above all others; so that, observing the command which was given him, his continuance should be to eternity. This God,-Father, Son, and Holy Ghost, which is an undivided Trinity,- mankind, from the east unto the west, by confession of faith to the saving of their souls, do worship and adore as the Creator of all things, and their own Maker; to whom also the heights of empire, and the powers of the world, are subject, because the bestowal of all kingdoms is granted by his disposition. It hath pleased Him, therefore, of his great mercy, and for the greater benefit of all his creatures, by his Holy Spirit wonderfully to kindle the cold hearts also of the nations seated at the extremities of the earth in the knowledge of Himself.
[. . .]
How great guilt they lie under, who adhere to the pernicious superstitions and worship of idolatry, appears by the examples of the perdition of those whom they worship. Wherefore it is said of them by the Psalmist, 'All the gods of the Gentiles are devils, but the Lord made the heavens.' And again, 'they have eyes and do not see, they have ears and do not hear, they have noses and do not smell, they have hands and do not feel, they have feet and do not walk. Therefore they are like those that confide in them.' For how can they have any power to yield assistance, that are made for you out of corruptible matter, by the hands of your inferiors and subjects, to wit, on whom you have by human art bestowed an inanimate similitude of members? Who, unless they be moved by you, will not be able to walk; but, like a stone fixed in one place, being so formed, and having no understanding, but absorbed in insensibility, have no power of doing harm or good. We cannot, therefore, upon mature deliberation, find out how you come to be so deceived as to follow and worship those gods, to whom you yourselves have given the likeness of a body.
It behooves you, therefore, by taking upon you the sign of the holy cross, by which the human race is redeemed, to root out of your hearts all those arts and cunning of the Devil, who is ever jealous of the works of the Divine goodness, and to lay hold and break in pieces those which you have hitherto made your material gods. For the very destruction and abolition of these, which could never receive life or sense from their makers, may plainly demonstrate to you how worthless they were which you till then had worshipped, when you yourselves, who have received life from the Lord, are certainly better than they, as-Almighty God has appointed you to be descended after many ages and through many generations, from the first man whom He formed. Draw near, then, to the knowledge of Him who created you, who breathed the breath of life into you, who sent his only-begotten Son for your redemption, to cleanse you from original sin, that being delivered from the power of the Devil's wickedness, He might bestow on you a heavenly reward.
Hear the words of the preachers, and the Gospel of God, which they declare to you, to the end that, believing, as has been said, in God the Father Almighty, and in Jesus Christ his Son, and the Holy Ghost, and the indivisible Trinity, having put to flight the sensualities of devils, and driven from you the suggestions of the venomous and deceitful enemy, and being born again by water and the Holy Ghost, you may, through his assistance and bounty, dwell in the brightness of eternal glory with Him in whom you shall believe. We have, moreover, sent you the blessing of your protector, the blessed Peter, prince of the apostles, that is, a shirt, with one gold ornament, and one garment of Ancyra, which we pray your highness to accept with the same goodwill as it is friendly intended by us."
CHAPTER XI
POPE BONIFACE ADVISES QUEEN ETHELBERGA TO USE HER BEST ENDEAVOURS FOR THE SALVATION OF HER CONSORT, KING EDWIN. [A.D. 625.]
THE same pope also wrote to King Edwin's Consort, Ethelberga, to this effect
THE COPY OF THE LETTER OF THE MOST BLESSED AND APOSTOLIC BONIFACE, POPE OF THE CITY OF ROME, TO ETHELBERGA, KING EDWIN'S QUEEN.
"To the illustrious lady his daughter, Queen Ethelberga, Boniface, bishop, servant of the servants of God: The goodness of our Redeemer has with much providence offered the means of salvation to the human race; which He rescued, by the shedding of his precious blood, from the bonds of captivity to the Devil; so that making his name known in divers ways to the Gentiles, they might acknowledge their Creator by embracing the mystery of the Christian faith, which thing, the mystical purification of your regeneration plainly shows to have been bestowed upon the mind of your highness by God's bounty. Our mind, therefore, has been much rejoiced in the benefit of our Lord's goodness, for that He has vouchsafed, in your conversion, to kindle a spark of the orthodox religion, by which He might the more easily inflame in his love the understanding, not only of your glorious consort, but also of all the nation that is subject to you.
For we have been informed by those, who came to acquaint us with the laudable conversion of our illustrious son, King Eadbald, that your highness, also, having received the wonderful sacrament of the Christian faith, continually excels in the performance of works pious and acceptable to God. That you likewise carefully refrain from the worship of idols, and the deceits of temples and auguries, and having changed your devotion, are so wholly taken up with the love of your Redeemer, as never to cease lending your assistance for the propagation of the Christian faith. And our fatherly charity having earnestly inquired concerning your illustrious husband, we were given to understand that he still served abominable idols, and would not yield obedience or give ear to the voice of the preachers. This occasioned us no small grief, for that part of your body still remained a stranger to the knowledge of the supreme and undivided Trinity. Whereupon we, in our fatherly care, did not delay to admonish your Christian highness, exhorting you, that, with the help of the Divine inspiration, you will not defer to do that which, both in season and out of season, is required of us; that with the co-operating power of our Lord and Saviour Jesus Christ, your husband also may be added to the number of Christians; to the end that you may thereby enjoy the rights of marriage in the bond of a holy and unblemished union. For it is written, 'They two shall be in one flesh How can it be said, that there is unity between you, if he continues a stranger to the brightness of your faith, by the interposition of dark and detestable error?
Wherefore, applying yourself continually to prayer, do not cease to beg of the Divine Mercy the benefit of his illumination; to the end, that those whom the union of carnal affection has made in a manner but one body, may, after death, continue in perpetual union, by the bond of faith. Persist, therefore, illustrious daughter, and to the utmost of your power endeavour to soften the hardness of his heart by insinuating the Divine precepts; making him sensible how noble the mystery is which you have received by believing, and how wonderful is the reward which, by the new birth, you have merited to obtain. Inflame the coldness of his heart by the knowledge of the Holy Ghost, that by the abolition of the cold and pernicious worship of paganism, the heat of Divine faith may enlighten his understanding through your frequent exhortations; that the testimony of the holy Scripture may appear the more conspicuous, fulfilled by you, 'The unbelieving husband shall be saved by the believing wife.' For to this effect you have obtained the mercy of our Lord's goodness. that you may return with increase the fruit of faith, and the benefits entrusted in your hands; for through the assistance of his mercy we do not cease with frequent prayers to beg that you may be able to perform the same.
Having premised thus much, in pursuance of the duty of our fatherly affection, we exhort you, that when the opportunity of a bearer shall offer, you will as soon as possible acquaint us with the success which the Divine Power shall grant by your means in the conversion of your consort, and of the nation subject to you; to the end, that our solicitude, which earnestly expects what appertains to the salvation of you and yours, may, by hearing from you, be set at rest; and that we, discerning more fully the brightness of the Divine propitiation diffused in you, may with a joyful confession abundantly return due thank to God, the Giver of all good things, and to St. Peter the prince of apostles. We have, moreover, sent you the blessing of your protector, St. Peter, the prince of the apostles, that is, a silver looking-glass, and a gilt ivory comb, which we entreat your glory will receive with the same kind affection as it is known to be sent by us."
[. . .]
CHAPTER XIII
OF THE COUNCIL HE HELD WITH HIS CHIEF MEN ABOUT EMBRACING THE FAITH OF CHRIST, AND HOW THE HIGH PRIEST PROFANED HIS OWN ALTARS. [A.D. 627.]
THE king, hearing these words, answered, that he was both willing and bound to receive the faith which he taught; but that he would confer about it with his principal friends and counsellers, to the end that if they also were of his opinion, they might all. together be cleansed in Christ the Fountain of Life. Paulinus consenting, the king did as he said; for, holding a council with the wise men, he asked of every one in particular what he thought of the new doctrine, and the new worship that was preached? To which the chief of. his own priests, Coifi, immediately answered, "O king, consider what this is which is now preached to us; for I verily declare to you, that the religion which we have hitherto professed has, as far as I can learn, no virtue in it. For none of your people has applied himself more diligently to the worship of our gods than I; and yet there are many who receive greater favours from you, and are more preferred than I, and are more prosperous in all their undertakings. Now if the gods were good for any thing, they would rather forward me, who have been more careful to serve them. It remains, therefore, that if upon examination you find those new doctrines, which are now preached to us, better and more efficacious, we immediately receive them without any delay."
Another of the king's chief men, approving of his words and exhortations, presently added: "The present life of man, O king, seems to me, in comparison of that time which is unknown to us, like to the swift flight of a sparrow through the room wherein you sit at supper in winter, with your commanders and ministers, and a good fire in the midst, whilst the storms of rain and snow prevail abroad; the sparrow, I say, flying in at one door, and immediately out at another, whilst he. is within, is safe from the wintry storm; but after a short space of fair weather, he immediately vanishes out of your sight, into the dark winter from which he had emerged. So this life of man appears for a short space, but of what went before, or what is to follow, we are utterly ignorant. If, therefore, this new doctrine contains something more certain, it seems justly to deserve to be followed." The other elders and king's councillors, by Divine inspiration, spoke to the same effect.
But Coifi added, that he wished more attentively to bear Paulinus discourse concerning the God whom he preached; which he having by the king's command performed, Coifi, hearing his words, cried out, "I have long since been sensible that there was nothing in that which we worshipped; because the more diligently I sought after truth in that worship, the less I found it. But now I freely confess, that such truth evidently appears in this preaching as can confer on us the gifts of life, of salvation, and of eternal happiness. For which reason I advise, O king, that we instantly abjure and set fire to those temples and altars which we have consecrated without reaping any benefit from them." In short, the king publicly gave his licence to Paulinus to preach the Gospel, and renouncing idolatry, declared that he received the faith of Christ: and then he inquired of the high priest who should first profane the altars and temples of their idols, with the enclosures that were about them, he answered, "I; for who can more properly than myself destroy those things which I worshipped through ignorance, for an example to all others, through the wisdom which has been given me by the true God?" Then immediately, in contempt of his former superstitions, he desired the king to furnish him with arms and a stallion; and mounting the same, he set out to destroy the idols; for it was not lawful before for the high priest either to carry arms, or to ride on any but a mare. Having, therefore, girt a sword about him, with a spear in his hand, he mounted the king's stallion and proceeded to the idols. The multitude, beholding it, concluded he was distracted; but he lost no time, for as soon as he drew near the temple he profaned the same, casting into it the spear which he held; and rejoicing in the knowledge of the worship of the true God, he commanded his companions to destroy the temple, with all its enclosures, by fire. This place where the idols were is still shown, not far from York, to the eastward, beyond the river Derwent, and is now called Godmundinghan, where the high priest, by the inspiration of the true God, profaned and destroyed the altars which he had himself consecrated.
CHAPTER XIV
KING EDWIN AND HIS NATION BECOME CHRISTIANS; PAULINUS BAPTIZES THEM. [A.D. 627.]
KING EDWIN, therefore, with all the nobility of the nation, and a large number of the common sort, received the faith, and the washing of regeneration, in the eleventh year of his reign, which is the year of the incarnation of our Lord 627, and about one hundred and eighty after the coming of the English into Britain. He was baptized at York, on the holy day of Easter, being the 12th of April, in the church of St. Peter the Apostle, which he himself had built of timber, whilst he was catechising and instructing In order to receive baptism. In that city also he appointed the see of the bishopric of his instructor and bishop, Paulinus. But as soon as he was baptized, he took care, by the direction of the same Paulinus, to build in the same place a larger and nobler church of stone, in the midst whereof that same oratory which he had first erected should be enclosed. Having therefore laid the foundation, he began to build the church square, encompassing the former oratory. But before the whole was raised to the proper height, the wicked assassination of the king left that work to be finished by Oswald his successor. Paulinus, for the space of six years from that time, that is, till the end of the reign of that king, by his consent and favour, preached the word of God in that Country, and all that were preordained to eternal life believed and were baptized. Among whom were Osfrid and Eadfrid, King Edwin's sons, who were both born to him, whilst he was in banishment, of Quenberga, the daughter of Ceari, king of the Mercians.
Afterwards other children of his by Queen Ethelberga were baptized, Ethelhun and his daughter Etheidrith, and another, Wuscfrea, a son; the first two of which were snatched out of this life whilst they were still in their white garments, and buried in the church at York. Ifli, the son of Osfrid, was also baptized, and many more noble and illustrious persons. So great was then the fervour of the faith, as is reported, and the desire of the washing of salvation among the nation of the Northumbrians, that Paulinus at a certain time coming with the king and queen the royal country-seat, which is called Adgefrin, stayed there with them thirty-six days, fully occupied in catechising and baptizing; during which days, from morning till night, he did nothing else but instruct the people resorting from all villages and places, in Christ's saving word; and when instructed, he washed them with the water of absolution in the river Glen, which is close by. This town, under the following kings, was abandoned, and another was built intead of it, at the place called Melmin.
These things happened in the province of the Bernicians; but in that of the Deiri also, where he was wont often to be with the king, he baptized in the river Swale, which runs by the village of Cataract; for as yet oratories, or fonts, could not be made in the early infancy of the church in those parts. But he built a church in Campodonum, which afterwards the pagans, by whom King Edwin was slain, burnt, together with all the town. In the place of which the later kings built themselves a country-seat in the Country called Loidis. But the altar, being of stone, escaped the fire and is still preserved in the monastery of the most reverend abbot and priest, Thridwulf, which is in Elsiete wood.
Footnotes
[1] Edwin was king of Northumbria from 616-633.
[2] This marriage appears to be an alliance between the families of Edwin and Eadbald, the brother of Ethelberga.
Tags recommended by the template: article:topic-category

