9.7: Inductive and Deductive Reasoning
- Page ID
- 58382
- Differentiate between deductive and inductive reasoning
Deductive and Inductive Arguments: Two Ways of Understanding
We have two basic approaches for how we come to believe something is true.
The first way is that we are exposed to several different examples of a situation, and from those examples, we conclude a general truth. For instance, you visit your local grocery store daily to pick up necessary items. You notice that on Friday, two weeks ago, all the clerks in the store were wearing football jerseys. Again, last Friday, the clerks wore their football jerseys. Today, also a Friday, they’re wearing them again. From just these observations, you can conclude that on all Fridays, these supermarket employees will wear football jerseys to support their local team.
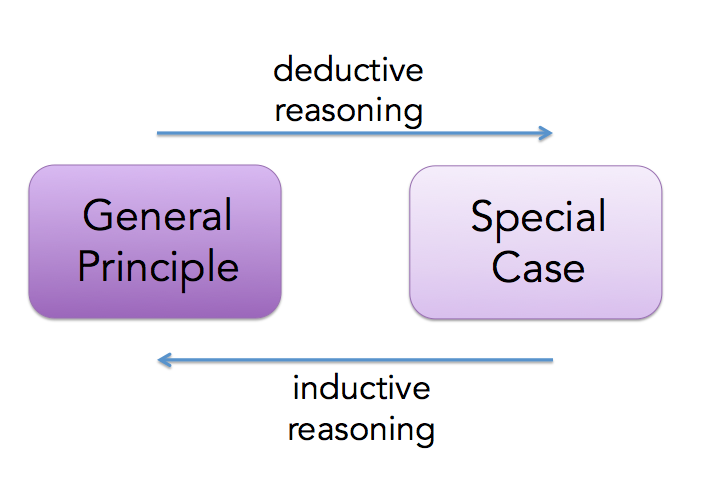
This type of pattern recognition, leading to a conclusion, is known as inductive reasoning.
Knowledge can also move the opposite direction. Say that you read in the news about a tradition in a local grocery store, where employees wore football jerseys on Fridays to support the home team. This time, you’re starting from the overall rule, and you would expect individual evidence to support this rule. Each time you visited the store on a Friday, you would expect the employees to wear jerseys.
Such a case, of starting with the overall statement and then identifying examples that support it, is known as deductive reasoning.
Deduction
In the process of deduction, you begin with some statements, called “premises,” that are assumed to be true, you then determine what else would have to be true if the premises are true.
For example, you could begin by assuming that God exists, and is good, and then determine what would logically follow from such an assumption. With this premise, you would look for evidence supporting a belief in God.
With deduction, you can provide absolute proof of your conclusions, given that your premises are correct. The premises themselves, however, remain unproven and unprovable.
Examples of deductive logic:
- All men are mortal. Joe is a man. Therefore Joe is mortal. If the first two statements are true, then the conclusion must be true.
- Bachelors are unmarried men. Bill is unmarried. Therefore, Bill is a bachelor.
- To get a Bachelor’s degree at a college, a student must have 120 credits. Sally has more than 130 credits. Therefore, Sally has a bachelor’s degree.
Induction
In the process of induction, you begin with some data, and then determine what general conclusion(s) can logically be derived from those data. In other words, you determine what theory or theories could explain the data.
For example, you note that the probability of becoming schizophrenic is greatly increased if at least one parent is schizophrenic, and from that you conclude that schizophrenia may be inherited. That is certainly a reasonable hypothesis given the data.
However, induction does not prove that the theory is correct. There are often alternative theories that are also supported by the data. For example, the behavior of the schizophrenic parent may cause the child to be schizophrenic, not the genes.
What is important in induction is that the theory does indeed offer a logical explanation of the data. To conclude that the parents have no effect on the schizophrenia of the children is not supportable given the data, and would not be a logical conclusion.
Examples of inductive logic:
- This cat is black. That cat is black. A third cat is black. Therefore all cats are black.
- This marble from the bag is black. That marble from the bag is black. A third marble from the bag is black. Therefore all the marbles in the bag black.
- Most universities and colleges in Utah ban alcohol from campus. Therefore most universities and colleges in the U.S. ban alcohol from campus.
Deduction and induction by themselves are inadequate to make a compelling argument. While deduction gives absolute proof, it never makes contact with the real world, there is no place for observation or experimentation, and no way to test the validity of the premises. And, while induction is driven by observation, it never approaches actual proof of a theory. Therefore an effective paper will include both types of logic.

This video reviews some of the distinctions between inductive and deductive reasoning.
You can view the transcript for “Inductive VS Deductive Reasoning by Shmoop” here (opens in new window).
deductive reasoning: top-down reasoning; a method of reasoning in which a certain conclusion follows general premises.
inductive reasoning: bottom-up reasoning; a method of reasoning in which several premises provide evidence of a probable conclusion.
Contributors and Attributions
- Image of inductive and deductive reasoning. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Argument Terminology. Authored by: Farcaster. Located at: https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Argument#/media/File:Argument_terminology_used_in_logic.png. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Inductive VS Deductive Reasoning by Shmoop. Authored by: Shmoop. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VXW5mLE5Y2g&feature=youtu.be. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- Inductive and Deductive Reasoning. Provided by: Utah State University. Located at: ocw.usu.edu/English/introduction-to-writing-academic-prose/inductive-and-deductive-reasoning.html. Project: English 1010 Handbook. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- The Logical Structure of Arguments. Authored by: Radford University. Located at: lcubbison.pressbooks.com/chapter/core-201-analyzing-arguments/. Project: Core Curriculum Handbook. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright


