7.2: Use patterns of organization and development
- Page ID
- 15699
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Patterns of organization can help your readers follow the ideas within your essay and your paragraphs, but they can also work as methods of development to help you recognize and further develop ideas and relationships in your writing. Here are some strategies that can help you with both organization and development in your essays.
Major Patterns of Organization
Read the following sentences:
- Now take the pie out of the oven and let it cool on the stovetop.
- Mix the dry ingredients with the liquid ingredients.
- Set the pie crust aside while you make the filling.
How did it feel to read the above list? A bit confusing, I would guess. That’s because the steps for making a pie were not well organized, and the steps don’t include enough detail for us to know exactly what we should do. (Like what are the dry and liquid ingredients?) We all know that starting instructions from the beginning and giving each detailed step in the order it should happen is vital to having a good outcome, in this case a yummy pie! But it’s not always so simple to know how to organize or develop ideas, and sometimes there’s more than one way, which complicates things even further.
First, let’s take a look at a couple of ways to think about organization.
General to Specific or Specific to General
It might be useful to think about organizing your topic like a triangle:
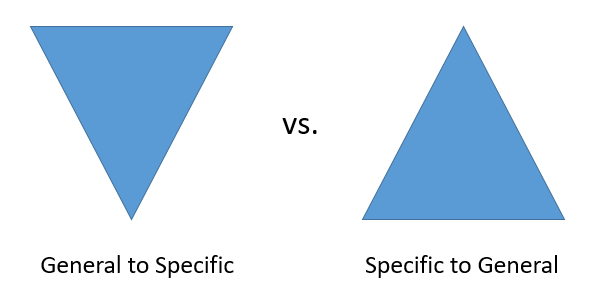
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)
The first triangle represents starting with the most general, big picture information first, moving then to more detailed and often more personal information later in the paper. The second triangle represents an organizational structure that starts with the specific, small scale information first and then moves to the more global, big picture stuff.
For example, if your topic is air pollution in Portland, Oregon, an essay that uses the general-to-specific organizational structure might begin this way:
Many people consider Portland, Oregon, to be an environmentally friendly, pollution-free place to live. They would be shocked to know how many pollutants are in the air causing a multitude of health problems in Portland’s citizens.
An essay that uses the specific-to-general structure might start like this:
When Nancy moved to Portland, Oregon, with her husband and two kids, she expected to find a clean, pollution-free city. She was shocked and angered when her daughter was diagnosed with asthma caused by air pollution.
What’s the difference between these two introductions? And how might they appeal to the intended audience for this essay (Portland voters) in different ways? The first introduction is looking at the big picture of the problem and mentions pollution’s impact on all citizens in Portland, while the second introduction focuses on one specific family. The first helps readers see how vast the problem really is, and the second helps connect readers to a real family, making an emotional appeal from the very beginning. Neither introduction is necessarily better. You’ll choose one over the other based on the kind of tone you’d like to create and how you’d like to affect your audience. It’s completely up to you to make this decision.
Does the Triangle Mean the Essay Keeps Getting More Specific or More Broad until the Very End?
The triangle is kind of a general guide, meaning you’re allowed to move around within it all you want. For example, it’s possible that each of your paragraphs will be its own triangle, starting with the general or specific and moving out or in. However, if you begin very broadly, it might be effective to end your essay in a more specific, personal way. And if you begin with a personal story, consider ending your essay by touching on the global impact and importance of your topic.
Are There Other Ways to Think about Organizing My Ideas?
Yes! Rather than thinking about which of your ideas are most specific or personal or which are more broad or universal, you might consider one of the following ways of organizing your ideas:
- Most important information first (consider what you want readers to focus on first)
- Chronological order (the order in time that events take place)
- Compare and contrast (ideas are organized together because of their relationship to each other)
The section on Methods of Development, below, offers more detail about some of these organizational patterns, along with some others.
Exercise

Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Choose one of the following topics, and practice writing a few opening sentences like we did above, once using the general-to-specific format and once using the specific-to-general. Which do you like better? What audience would be attracted to which one? Share with peers to see how others tackled this challenge. How would you rewrite their sentences? Why? Discuss your changes and listen to how your peers have revised your sentences. Taking in other people’s ideas will help you see new ways to approach your own writing and thinking.
Topics:
- Facing fears
- Safety in sports
- Community policing
- Educating prisoners
- Sex education
- A book or movie that impacted you
- One thing you would change about your community
- Beauty standards
- Toxic masculinity
- How the media affects identity formation
- Gender roles
- Race in America
- The value of art in society
- Travel as part of a well-rounded education
- Drugs and alcohol
- Advice to new parents
- Advice to teachers
- The value of making mistakes
- How you’d spend a million dollars
- What a tough day at work taught you about yourself or others.
Methods of Development
The methods of development covered here are best used as ways to look at what’s already happening in your draft and to consider how you might emphasize or expand on any existing patterns. You might already be familiar with some of these patterns because teachers will sometimes assign them as the purpose for writing an essay. For example, you might have been asked to write a cause-and-effect essay or a comparison-and-contrast essay.
It’s important to emphasize here that patterns of organization or methods of developing content usually happen naturally as a consequence of the way the writer engages with and organizes information while writing. That is to say, most writers don’t sit down and say, “I think I’ll write a cause-and-effect essay today.” Instead, a writer might be more likely to be interested in a topic, say, the state of drinking water in the local community, and as the writer begins to explore the topic, certain cause-and-effect relationships between environmental pollutants and the community water supply may begin to emerge.
So if these patterns just occur naturally in writing, what’s the use in knowing about them? Well, sometimes you might be revising a draft and notice that some of your paragraphs are a bit underdeveloped. Maybe they lack a clear topic, or maybe they lack support. In either case, you can look to these common methods of development to find ways to sharpen those vague topics or to add support where needed. Do you have a clear cause statement somewhere but you haven’t explored the effects? Are you lacking detail somewhere where a narrative story or historical chronology can help build reader interest and add support? Are you struggling to define an idea that might benefit from some comparison or contrast? Read on to consider some of the ways that these strategies can help you in revision. And if you want to learn more, check out what the New York Times has to say in their learning blog article, “Compare-Contrast, Cause-Effect, Problem Solution: Common ‘Text Types’ in The Times.”
Cause and Effect (or Effect and Cause)
Do you see a potential cause-and-effect relationship developing in your draft? The cause-and-effect pattern may be used to identify one or more causes followed by one or more effects or results. Or you may reverse this sequence and describe effects first and then the cause or causes. For example, the causes of water pollution might be followed by its effects on both humans and animals. You may use obvious transitions to clarify cause and effect, such as “What are the results? Here are some of them…” or you might simply use the words cause, effect, and result, to cue the reader about your about the relationships that you’re establishing.
Here’s an example article from the New York times, “Rough Times Take Bloom Off a New Year’s Rite, the Rose Parade,” that explores the cause and effect relationship (from 2011) between Pasadena’s budgetary challenges and the ability of their Rose Parade floats to deck themselves out in full bloom.
Problem-Solution
At some point does your essay explore a problem or suggest a solution? The problem-solution pattern is commonly used in identifying something that’s wrong and in contemplating what might be done to remedy the situation. There are probably more ways to organize a problem-solution approach, but but here are three possibilities:
- Describe the problem, followed by the solution.
- Propose the solution first and then describe the problems that motivated it.
- Or a problem may be followed by several solutions, one of which is selected as the best.
When the solution is stated at the end of the paper, the pattern is sometimes called the delayed proposal. For a hostile audience, it may be effective to describe the problem, show why other solutions do not work, and finally suggest the favored solution. You can emphasize the words problem and solution to signal these sections of your paper for your reader.
Here’s an example article from the New York times, “Monks Embrace Web to Reach Recruits,” that highlights an unexpected approach by a group of Benedictine monks in Rhode Island; they’ve turned to social media to grow their dwindling membership. Monks on Facebook? Who knew?
Chronology or Narrative
Do you need to develop support for a topic where telling a story can illustrate some important concept for your readers? Material arranged chronologically is explained as it occurs in time. A chronological or narrative method of development might help you find a way to add both interest and content to your essay. Material arranged chronologically is explained as it occurs in time. This pattern may be used to establish what has happened. Chronology or narrative can be a great way to introduce your essay by providing a background or history behind your topic. Or you may want to tell a story to develop one or more points in the body of your essay. You can use transitional words like then, next, and finally to make the parts of the chronology clear.
Here’s an example article from the Center for Media Literacy (originally published in the journal Media & Values): “From Savers to Spenders: How Children Became a Consumer Market.” To encourage his readers to think about why and how children are being marketed to by advertisers, the author uses a historical chronology of how the spending habits of children changed over a number of decades.
Comparison and Contrast
Are you trying to define something? Do you need your readers to understand what something is and what it is not? The comparison-and-contrast method of development is particularly useful in extending a definition, or anywhere you need to show how a subject is like or unlike another subject. For example, the statement is often made that drug abuse is a medical problem instead of a criminal justice issue. An author might attempt to prove this point by comparing drug addiction to AIDS, cancer, or heart disease to redefine the term “addiction” as a medical problem. A statement in opposition to this idea could just as easily establish contrast by explaining all the ways that addiction is different from what we traditionally understand as an illness. In seeking to establish comparison or contrast in your writing, some words or terms that might be useful are by contrast, in comparison, while, some, and others.
Here’s an example article from the New York times: “Who Wants to Shop in a Big Box Store, Anyway?” The author explores some interesting differences between the average American and average Indian consumer to contemplate the potential success of big box stores in India and also to contemplate why these giant big box corporations, like Walmart or Target, might have to rethink their business model.
These four methods of development—cause and effect, problem-solution, chronology or narrative, and comparison and contrast—are just a few ways to organize and develop ideas and content in your essays. It’s important to note that they should not be a starting point for writers who want to write something authentic—something that they care deeply about. Instead, they can be a great way to help you look for what’s already happening with your topic or in a draft, to help you to write more, or to help you reorganize some parts of an essay that seem to lack connection or feel disjointed. Look for organizational patterns when you’re reading work by professional writers. Notice where they combine strategies (e.g a problem-solution pattern that uses cause-and-effect organization, or a comparison-contrast pattern that uses narrative or chronology to develop similarities or differences). Pay attention to how different writers emphasize and develop their main ideas, and use what you find to inspire you in your own writing. Better yet, work on developing completely new patterns of your own.

