1.3.1: Present Progressive
- Page ID
- 268922
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)At the end of this chapter you should be able to:
- Recognize and use the present progressive:
- in the affirmative and negative
- with contractions
- with yes/no questions and short answers
- with information questions using appropriate wh-question words
- with time expressions
- with the correct spelling
Shopping for Food
Prepare
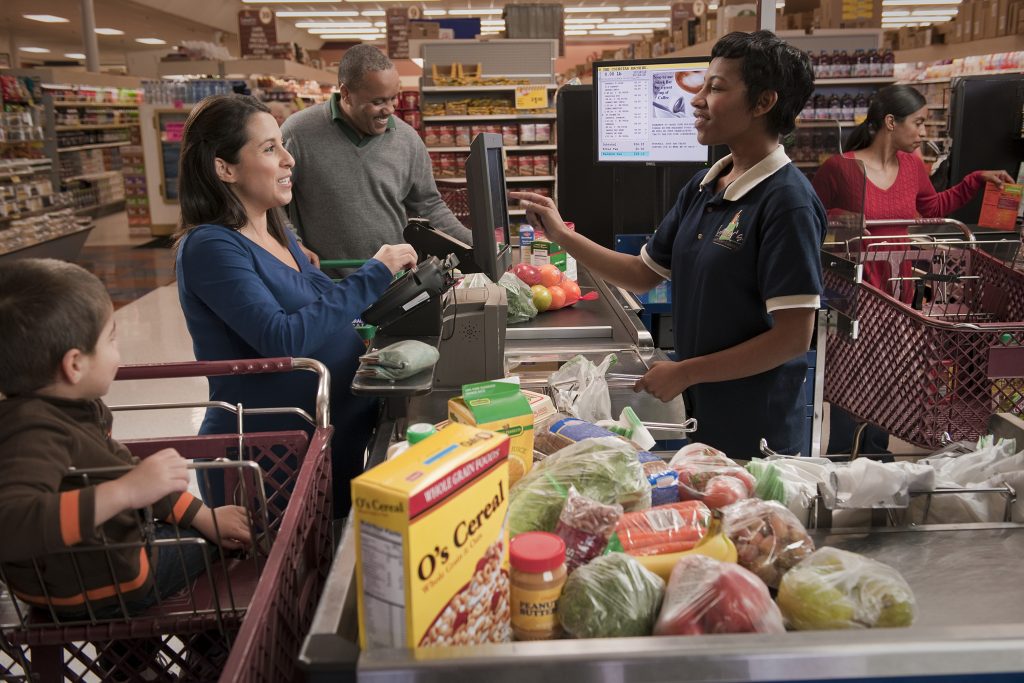

Directions: Look at the picture. What do you see? Write the words below.
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
Directions: Discuss the following questions with a partner.
- Where do you go grocery shopping?
- How often do you go grocery shopping?
- What do you buy at the grocery store?
- How do you get to the grocery store? Do you walk, go by car, or by bus?
Directions: Read this story out loud with a partner. One person reads a paragraph, then the other person reads the next paragraph. When you are finished, read the story again. This time, read the paragraphs you did not read.
Viktor and Tatiana Are Grocery Shopping
Viktor and Tatiana are from Ukraine. They are married. They are students at San Jacinto College, and they are taking ESOL classes this semester.
They are studying English so they can get jobs. They are not working now. Today, they need* to go to the grocery store. Right now, it is 3:00 pm.
They are walking to the grocery store, and it is raining hard. Viktor is holding an umbrella, so they are not getting wet. It is now 3:15 pm. They are
shopping for food and talking about their English classes. Tatiana remembers, “Oh! We need* pencils and paper.” Viktor says, “I want* some
erasers, too.”
Now, at 3:45 pm, they are waiting in line at checkout. The man at the front of the line is writing a check slowly. The baby in the cart behind
them is crying. At 3:55 pm, it is finally their turn. They are buying food and school supplies. A young man is putting their groceries in paper bags. Tatiana
is paying with cash. The cashier is giving them change and the receipt. It is 4:00 pm now. They are walking home. At this moment, it is not raining,
The sun is shining, and they are smiling.
Note
*Some verbs like “need” and “want” are called stative verbs. They show a state of being, not an action. Stative verbs are not used in the progressive tenses.
Directions: Answer the questions about the story.
1. Where are Viktor and Tatiana from? (Use the BE verb)
_________________________________________________________________________
2. Are they working this semester? (choose one)
Yes, they are. No, they aren’t.
3. What are they studying?
_________________________________________________________________________
4. What are they doing at 3:00 pm?
_________________________________________________________________________
5. What is the weather like?
_________________________________________________________________________
6. Are they getting wet? (choose one)
Yes, they are. / No, they aren’t.
7. What does Tatiana remember?
_________________________________________________________________________
8. What are they doing at 3:45 pm?
_________________________________________________________________________
9. Is the man paying cash? (chose one)
Yes, he is. / No, he isn’t.
10. What are Viktor and Tatiana doing at 4:00 pm?
_________________________________________________________________________
Explore
Directions: Read the story again. choose (by underlining or otherwise marking) all uses of the present progressive. Then, write three of the verbs used in the story below.
Remember
The present progressive tense has TWO parts: the auxiliary verb BE and the main verb plus "-ing".
are taking
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
Directions: Write three sentences using the verbs you found. Try to use ideas from the picture in Activity 2.1 above.
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
Discover
Uses of the Present Progressive
The present progressive is used to talk about an action or situation that is in progress and happening right now. It started in the past and is probably going to continue into the future. We often use time expressions (signal words) to show this: right now, at the/this moment, now.
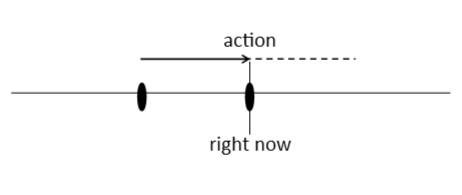
I am learning grammar right now.
Commentary: It is happening at this moment.
It also shows an action or situation that is continuing for a period around the present time. There are many expressions that show this: this week, this month, this year, this semester.
I am taking English classes this semester.
Commentary: It is happening around the present time.
The present progressive is also used to describe a change or temporary action.
I usually drive to school. This week, I am taking the bus.
Commentary: Notice that the simple present is used to talk about a habit/routine. The present progressive shows that there is a temporary change.
Time Expressions: Signals Words Used with the Present Progressive
We use time expressions to signal the time that the action is happening. Sometimes we call time expressions signal words.
- at the/this moment
- now
- right now
- this week/semester/month
At this moment, I am washing the dishes.
My husband is watching a football game right now.
Notice in the examples above that time expressions used with the present progressive can come at the beginning of a sentence or at the end of a sentence.
Forms of the Present Progressive
The present progressive is formed by an auxiliary (helping) verb and the main verb. The BE verb is the auxiliary for progressive tenses. It agrees with the subject (the person or thing that performs or completes the action of the verb; the “do-er”) and tells us that we are talking about the present time. The main verb changes by adding -ing to it. The -ing form of the main verb is called the present participle.
To form the present progressive tense, you need two parts of the verb:
auxiliary BE (am, is, are) + present participle (verb+ing)
| Subject | Auxiliary (Helping) Verb (BE) | Present Participle: Main Verb + -ing |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | writing |
| He/She/It | is | sleeping |
| You/ We/ They | are | watching |
Directions: Write about what is happening right now. Write three 3 sentences using present progressive and a time expression.
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
- _________________________________________________________________________
Spelling: Present Participle (-ing Verb Form)
Spelling in English can be difficult, but there are some rules to follow when forming the present participle.
Rule 1: If the base verb ends in a consonant + 1 vowel + consonant (CVC), double the consonant before adding -ing: hit → hitting. If there are two vowels between the consonants, do NOT double the last consonant: rain → raining.
| Base Verb | Present Participle |
|---|---|
| hit | hitting |
| plan | planning |
| run | running |
| stop | stopping |
| swim | swimming |
Rule 2: NEVER double the consonants w, x, or y (e.g., playing). The n is usually not doubled when verbs end in -en (e.g., happening).
Rule 3: If the base verb ends in an -e, remove it before adding -ing.
| Base Verb | Present Participle |
|---|---|
| come | coming |
| ride | riding |
| dance | dancing |
| write | writing |
| leave | leaving |
Directions: Change the base verbs to the present participle. Use the spelling rules to help you.
| Base Verb | Present Participle |
|---|---|
| take | 1. |
| study | 2. |
| get | 3. |
| wait | 4. |
| give | 5. |
| listen | 6. |
| sit | 7. |
| pay | 8. |
| shop | 9. |
| make | 10. |
Part 1 Directions: Complete the sentences with the correct form of the present progressive. Be sure and spell the verbs correctly as described above.
The present progressive has TWO parts: auxiliary BE and the present participle (the main verb + ing).
Viktor and Tatiana are new to the United States. They are students at San Jacinto College. They (1. take)__________________ ESOL classes this
semester. They (2. study)__________________ English, so they can get jobs. They love their classes. Right now, they (3. walk)__________________ to the
grocery store. It (4. rain) __________________ hard, so Viktor (5. hold)__________________ the umbrella to keep them dry.
Part 2 Directions: Now go back and choose (by underlining or otherwise marking) the time expressions. There are two.
Directions: Think about what you are doing right now. Work with a partner to write three sentences using the present progressive and time expressions. Every sentence should have a time expression. Check your spelling when you are done.
- ______________________________________________________
- ______________________________________________________
- ______________________________________________________
Affirmative in the Present Progressive
As noted above, we use the present progressive to talk about things happening now or around this time (extended time). The affirmative tense form is the BE verb + the present participle
subject + BE + present participle
| Subject | Auxiliary BE | Present Participle |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | shopping. |
| He/She/It | is | shopping. |
| You/We/They | are | shopping. |
Directions: Look at the grammar table above and fill in the table below with the missing parts of the sentence.
| Subject | Auxiliary BE | Present Participle |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | am | learning. (learn) |
| 2. He | is | (work) |
| 3. She | walking. (walk) | |
| 4. | is | raining. (rain) |
| 5. You | are | (read) |
| 6. We | sitting. (sit) | |
| 7. | are | running. (run) |
Affirmative Contractions in the Present Progressive
Contractions in the present progressive are formed just as we learned in Chapter 1. They are very common in spoken English.
| Subject | Auxiliary BE | Present Participle |
|---|---|---|
| I'm |
shopping. |
|
| He's She's It's |
||
| You're We're They're |
||
Directions: Take the sentences you completed in Activity 2.10 and write them on lined notebook paper using contractions. Then, write one (1) sentence of your own. Write your name, the date, and Assignment 2.11 at the top of your paper.
Directions: Look at the pictures. Then, answer the questions using the words given to you. Change the verb to the present progressive. Use full forms for odd numbers and contractions for even numbers.

1. What is the man doing?
he / make a grocery list
______________________________________________________

2. What is the man doing?
he / buy vegetables
________________________________________________________

3. What is the woman doing?
she / look at pineapples
__________________________________________________________

4. What is the man doing?
he / compare prices
___________________________________________________________

5. What is the woman doing?
she / wait for customers
____________________________________________________________

6. What is the man doing?
he / pay with a debit card
______________________________________________________________

7. What is the man doing?
he / check his grocery list
_______________________________________________________________

8. What are the people doing?
they / shop at the farmer’s market
___________________________________________________________________

9. What is the cashier doing?
she / smile at customers
_____________________________________________________________________

10. What is the man doing?
he / walk down the aisle
______________________________________________________________________
Directions: Complete the sentences with the present progressive form of the verb in parentheses.
- My son (come) ____________________home from school now.
- Right now, I (write)_________________ this sentence.
- At the moment, my wife (sit)_________________ on the sofa.
- They (buy)_________________ groceries at the market now.
- This week, we (study)_________________ the present progressive tense.
- The girl (do)_________________ her homework in the living room.
- You (think)___________________________about grammar as you do this exercise.
- The people at this party (wear)_________________ beautiful clothes.
- He (sing)_________________ a song in the shower now.
- This year, my son (play)_________________ the violin.
- The woman (feed)_________________ her cat.
- They (give)_________________ a reward to the brave man.
- The boys (draw)_________________ pictures in their notebooks.
- I (carry)_________________ my books to class right now.
- It (rain)_________________ very hard at the moment.
- We (listen)_________________ to the radio right now.
- You (answer)_________________ these questions now.
- The dog (chew)_________________ a shoe now.
- The boy’s mother (feel)_________________ sick today.
- The students (improve)_________________ their grammar this semester.
Adapted from: “ESL for Beginning Students: The Way You Like It Basic Beginning Grammar/Writing (Part One of Two)” by Don Bissonnette, licensed under CC BY-NC 4


