10.5: Culture
- Page ID
- 151364
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)In this section, you will:
- Learn about the Arab countries Tunisia and Algeria, their famous cities, their most famous historical places, their traditional food, and clothes.
10.5.1. Tunisia and Algeria
Tunisia and Algeria are part of the Maghreb region of the Middle East. The Maghreb countries are Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania.
10.5.2. Tunisia and Algeria
| The Country Name in English | The Country Name in Arabic | The Name of the Capital in English | The Name of the Capital in Arabic | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tunisia |
تونس Touness |
Tunis |
تونس Touness |
.svg.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=214&height=169)
|
| Algeria |
الجزائر Al-Jaza'er |
Algiers |
الجزائر Al-Jaza'er |
.svg.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=214&height=169)
|
10.5.3. Countries and Famous Cities
10.5.3.1. Tunisia
Tunisia is an Arab country located in north Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, north-east, and east, Algeria to the west and south-west, and Libya to the south-east.
Population: 11.82 million (2020 estimate).
Capital: Tunis.
Currency: Tunisian Dinar (TND).
Official Language: Modern Standard Arabic.
_-_TUN_-_UNOCHA.svg.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=550&height=550)
| City Name | City Name in Arabic | Pronunciation | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tunis | تونس | Touness |
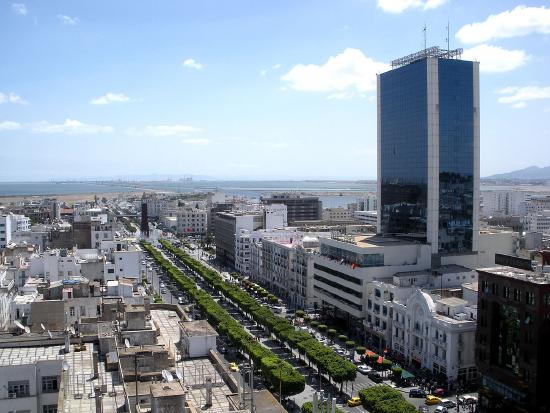

|
| Kairouan | القيروان | Al-Qayrawan |

|
| Sfax | صفاقس | Safakess |

|
| Sousse | سوسة | Soussah |

|
| Gabès | قابس | Qaabess |

|
| Ariana | أريانة | Arianah |
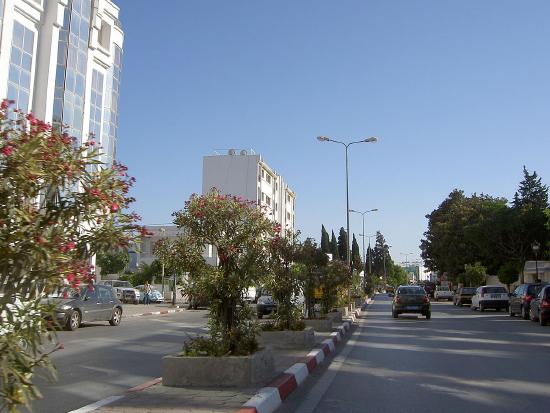

|
10.5.3.2. Algeria
Algeria is an Arab country located in north Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Morocco to the west and north-west, Mauritania to the west, Mali to the south-west, Niger to the south-east, Libya to the east, and Tunisia to the north-east.
Population: 43.85 million (2020 estimate).
Capital: Algiers.
Currency: Algerian Dinar (DZD).
Official Language: Modern Standard Arabic.
_-_DZA_-_UNOCHA.svg.png?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=550&height=550)
| City Name | City Name in Arabic | Pronunciation | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Algiers | الجزائر | Al-Jaza'er |
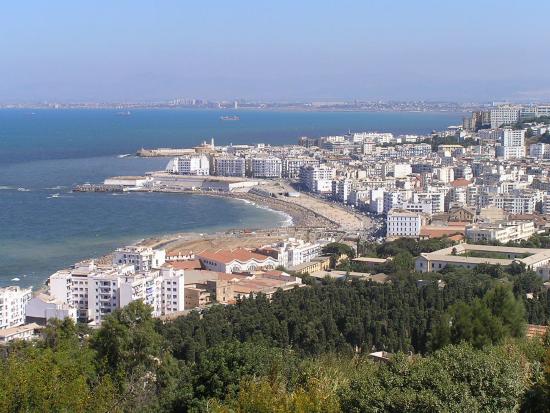

|
| Oran | وهران | Wahraan |

|
| Constantine | قسنطينة | Qsantinah |
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=214&height=169)
|
| Batna | باتنة | Batnah |

|
| Annaba | عنّابة | Annabah |

|
| Tlemcen | تلمسان | Tlemssen |
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=214&height=169)
|
10.5.4. Famous Historical Places
10.5.4.1. Tunisia
The video below presents a tour around Tunisia:
Carthage - Tunis
Carthage (Qertaaj - قرطاج) was the capital city of the Carthagian civilization north-east of Tunisia. It was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean. Carthage was founded in the 9th century BC on the Gulf of Tunis. Its remains now lie on the outskirts of Tunis, Tunisia.

El Jem Amphitheater - El Jem
El Jem Amphitheater (Masrah El-Jem - مسرح الجم) is located in the north-eastern part of Tunisia in the city of El Jem. It was built in 238 AD by the Roman Empire and was one of their biggest amphitheaters. It is an exceptionally welll-preserved amphitheater.

Bulla Regia - Jendouba
Bulla Regia (Bularigia - بولاريجيا) is an ancient town which was Berber, Punic, and Roman. It is located in the north-west of Tunisia near Jendouba. It emerged around the 5th century BC under Carthage. It is one of the most prominent historical sites in Tunisia.
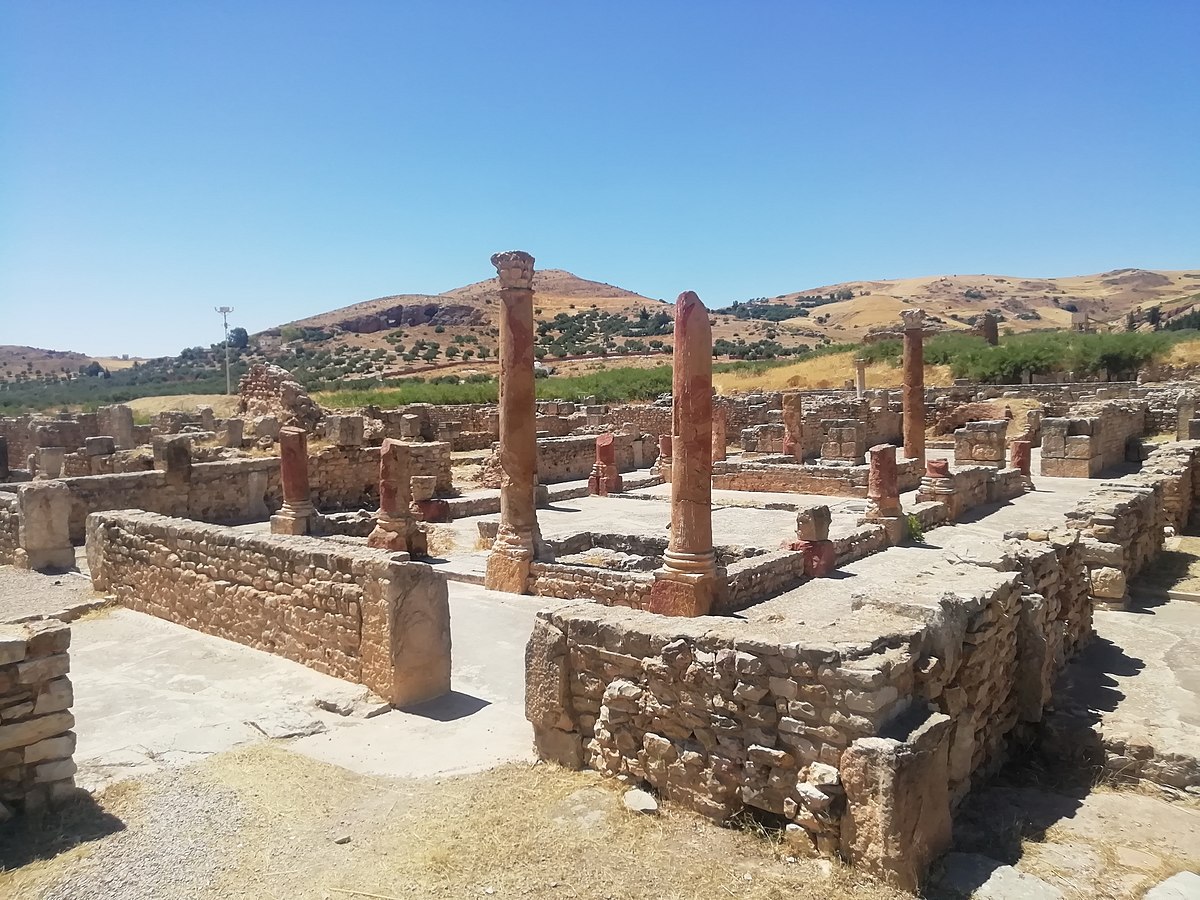

10.5.4.2. Algeria
The video below presents a tour around Algeria:
Notre Dame of Africa - Algiers
Notre Dame of Africa (Al-Saiyda Al-Ifriqiya - السيّدة الإفريقيّة) is located on the north side of Algiers, Algeria. It was inaugurated in 1872 and employed a Neo-Byzantine style.
.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=550&height=412)
Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania - Tipaza Province
The Royal Mausoleum of Mauretania (Al-Dhareeh Al-Malaki Al- Moritani - الضريح الملكي الموريتاني) is a funerary monument located on the road between Churchell and Algiers in Tipaza Province, Algeria. It is the tomb where the Numidian Berber King Juba II and the Queen Cleopatra Selene II, sovereigns of Numidia and Mauretania Caesariensis, were allegedly buried. The Mausoleum was founded in 3 BC.
Fort Santa Cruz - Oran
Fort Santa Cruz (Qal'et Santa Krooz - قلعة سانتا كروز) is one of three forts in Oran. It was built between 1577 and 1604 by the Spaniards on the Pic d'Aidour above Gulf of Oran in the Mediterranean Sea, at an elevation of above 400 metres.
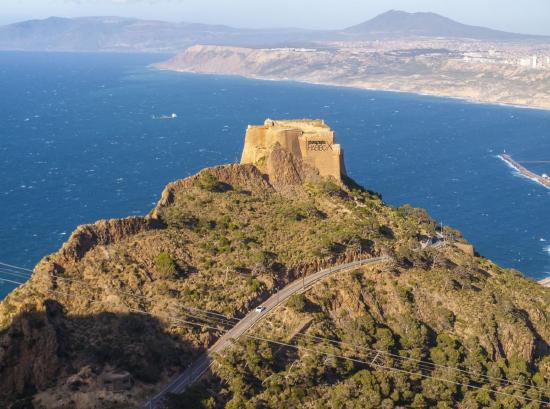

10.5.5. Traditional Food and Clothes
10.5.5.1. Traditional Food
The Maghreb countries have very delicious foods, some of which are found in common between them. While some remain the same from one Maghreb country to another, other vary in ingrediants and names.
| Region | Video |
|---|---|
| Traditional food in Tunisia | |
| Traditional food in Algeria |
| Food in English | Food in Arabic | Recipe | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shakshuka | شكشوكة |

|
|
| Couscous | كسكس |

|
|
| Brik | بريك |

|
|
| Harira Soup | شوربة حريرة |

|
10.5.5.2. Traditional Clothes
In each of the Maghreb countries, there are different traditional clothes that come as a result of different cultures and religious backgrounds of the different areas. This is why there is no single traditional clothing that we can call characteristic of the whole country. Traditional clothing is usually used in religious ceremonies, weddings, and/or other occasions, but is rarely, if at all, used in everyday life.
| Country | Clothes |
|---|---|
| Traditional clothing in Tunisia | |
| Traditional clothing in Algeria |
Put the name of the country under the correct flag:
Put the name of the city in the correct column:
Make a video about an Arab country. The video will include the following: Location, capital, famous cities, historical places, authentic dishes, and new Arabic Cultural phrases that you learned.

