1.3: Becoming a Successful Writer
- Page ID
- 4514
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Identify strategies for successful writing
- Demonstrate comprehensive writing skills
- Identify writing strategies for use in future classes
In the preceding sections, you learned what you can expect from your courses and identified strategies you can use to manage your work and to succeed. This section covers more about how to handle the demands placed on you as a writer at the post-secondary world. The general techniques you will learn will help ensure your success on any writing task, whether you complete an exam in an hour or an in-depth research project over several weeks.
Putting It All Together: Strategies for Success
Writing well is difficult. Even people who write for a living sometimes struggle to get their thoughts on the page. Even people who generally enjoy writing have days when they would rather be doing anything else. For people who do not like writing or do not think of themselves as good writers, writing assignments can be stressful or even intimidating. And of course, you cannot get through post-secondary courses without having to write—sometimes a lot, and often at a higher level than you are used to.
No magic formula will make writing quick and easy. However, you can use strategies and resources to manage writing assignments more easily. This section presents a broad overview of these strategies and resources. The remaining chapters of this book provide more detailed, comprehensive instruction to help you succeed at a variety of assignments.
Using the Writing Process
To complete a writing project successfully, good writers use some variation of the following process.
The Writing Process
Prewriting. The writer generates ideas to write about and begins developing these ideas.
Outlining a structure of ideas. The writer determines the overall organizational structure of the writing and creates an outline to organize ideas. Usually this step involves some additional fleshing out of the ideas generated in the first step.
Writing a rough draft. The writer uses the work completed in prewriting to develop a first draft. The draft covers the ideas the writer brainstormed and follows the organizational plan that was laid out in the first step.
Revising. The writer revisits the draft to review and, if necessary, reshape its content. This stage involves moderate and sometimes major changes: adding or deleting a paragraph, phrasing the main point differently, expanding on an important idea, reorganizing content, and so forth.
Editing. The writer reviews the draft to make additional changes. Editing involves making changes to improve style and adherence to standard writing conventions—for instance, replacing a vague word with a more precise one or fixing errors in grammar and spelling. Once this stage is complete, the work is a finished piece and ready to share with others.
Chances are you have already used this process as a writer. You may also have used it for other types of creative projects, such as developing a sketch into a finished painting or composing a song. The steps listed above apply broadly to any project that involves creative thinking. You come up with ideas (often vague at first), you work to give them some structure, you make a first attempt, you figure out what needs improving, and then you refine it until you are satisfied.
Most people have used this creative process in one way or another, but many people have misconceptions about how to use it to write. Here are a few of the most common misconceptions students have about the writing process:
“I do not have to waste time on prewriting if I understand the assignment.” Even if the task is straightforward and you feel ready to start writing, take some time to develop ideas before you plunge into your draft. Freewriting—writing about the topic without stopping for a set period of time—is one prewriting technique you might try in that situation.
“It is important to complete a formal, numbered outline for every writing assignment.” For some assignments, such as lengthy research papers, proceeding without a formal outline can be very difficult. However, for other assignments, a structured set of notes or a detailed graphic organizer may suffice. The important thing is to have a solid plan for organizing ideas and details.
“My draft will be better if I write it when I am feeling inspired.” By all means, take advantage of those moments of inspiration. However, understand that sometimes you will have to write when you are not in the mood. Sit down and start your draft even if you do not feel like it. If necessary, force yourself to write for just one hour. By the end of the hour, you may be far more engaged and motivated to continue. If not, at least you will have accomplished part of the task.
“My instructor will tell me everything I need to revise.” If your instructor chooses to review drafts, the feedback can help you improve. However, it is still your job, not your instructor’s, to transform the draft to a final, polished piece. That task will be much easier if you give your best effort to the draft before submitting it. During revision, do not just go through and implement your instructor’s corrections. Take time to determine what you can change to make the work the best it can be.
“I am a good writer, so I do not need to revise or edit.” Even talented writers still need to revise and edit their work. At the very least, doing so will help you catch an embarrassing typo or two. Revising and editing are the steps that make good writers into great writers.
Tip
The writing process also applies to timed writing tasks, such as essay exams. Before you begin writing, read the question thoroughly and think about the main points to include in your response. Use scrap paper to sketch out a very brief outline. Keep an eye on the clock as you write your response so you will have time to review it and make any needed changes before turning in your exam.
Managing Your Time
In Section 1.2, you learned general time management skills. By combining those skills with what you have learned about the writing process, you can make any writing assignment easier to manage.
When your instructor gives you a writing assignment, write the due date on your calendar. Then work backward from the due date to set aside blocks of time when you will work on the assignment. Always plan at least two sessions of writing time per assignment, so that you are not trying to move from step 1 to step 5 in one evening. Trying to work that fast is stressful, and it does not yield great results. You will plan better, think better, and write better if you space out the steps.
Ideally, you should set aside at least three separate blocks of time to work on a writing assignment: one for prewriting and outlining, one for drafting, and one for revising and editing. Sometimes those steps may be compressed into just a few days. If you have a couple of weeks to work on a paper, space out the five steps over multiple sessions. Long-term projects, such as research papers, require more time for each step.
Tip
In certain situations you may not be able to allow time between the different steps of the writing process. For instance, you may be asked to write in class or complete a brief response paper overnight. If the time available is very limited, apply a modified version of the writing process (as you would do for an essay exam). It is still important to give the assignment thought and effort. However, these types of assignments are less formal, and instructors may not expect them to be as polished as formal papers. When in doubt, ask the instructor about expectations, resources that will be available during the writing exam, and if he or she has any tips to prepare you to effectively demonstrate your writing skills.
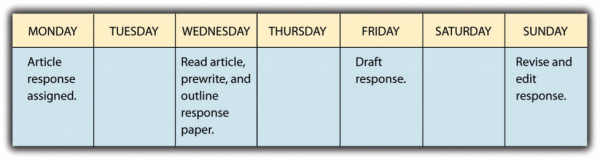
Each Monday in Crystal’s Foundations of Education class, the instructor distributed copies of a current news article on education and assigned students to write a one-and-a-half to two-page response that was due the following Monday. Together, these weekly assignments counted for 20 percent of the course grade. Although each response took just a few hours to complete, Crystal found that she learned more from the reading and got better grades on her writing if she spread the work out in the following way:
In this exercise, make connections between short– and long–term goals.
Review the long- and short-term goals you set for yourself for the discussion at the beginning of the module. Brainstorm a list of stepping stones that will help you meet that goal, such as “doing well on my midterm and final exams” or “talking to Professor Gibson about doing an internship.” Write down everything you can think of that would help you meet that semester goal.
Identify one action from Step 3 that you can do today. Then do it.
Using Available Resources
One reason students sometimes find post-secondary courses overwhelming is that they do not know about, or are reluctant to use, the resources available to them. There is help available; your student fees help pay for resources that can help in many ways, such as a health centre or tutoring service. If you need help, consider asking for help from any of the following:
Your instructor: If you are making an honest effort but still struggling with a particular course, set a time to meet with your instructor and discuss what you can do to improve. He or she may be able to shed light on a confusing concept or give you strategies to catch up.
Your academic counsellor. Many institutions assign students an academic counsellor who can help you choose courses and ensure that you fulfill degree and major requirements.
The academic resource centre: These centres offer a variety of services, which may range from general coaching in study skills to tutoring for specific courses. Find out what is offered at your school and use the services that you need.
The writing centre: These centres employ tutors to help you manage your writing assignments. They will not write or edit your paper for you, but they can help you through the stages of the writing process. (In some schools, the writing centre is part of the academic resource centre.)
The career resource centre: Visit the career resource centre for guidance in choosing a career path, developing a resumé, and finding and applying for jobs.
Counselling services: Many schools offer psychological counselling for free or for a low fee. Use these services if you need help coping with a difficult personal situation or managing depression, anxiety, or other problems.
Students sometimes neglect to use available resources due to limited time, unwillingness to admit there is a problem, or embarrassment about needing to ask for help. Unfortunately, ignoring a problem usually makes it harder to cope with later on. Waiting until the end of the semester may also mean fewer resources are available, since many other students are also seeking last minute help.
Identify at least one resource you think could be helpful to you and that you would like to investigate further. Schedule a time to visit this resource within the next week or two so you can use it throughout the semester.
Summary
You now have a solid foundation of skills and strategies you can use to succeed in university or college. The remainder of this book will provide you with guidance on specific aspects of writing, ranging from grammar and style conventions to how to write a research paper.
For any writing assignment, use these strategies:
- Plan ahead. Divide the work into smaller, manageable tasks, and set aside time to accomplish each task in turn.
- Make sure you understand the assignment requirements. If necessary, clarify the requirements with your instructor. Think carefully about the purpose of the writing, the intended audience, the topics you will need to address, and any specific requirements of the writing form.
- Complete each step of the writing process. With practice, using this process will come automatically to you.
- Use the resources available to you. Remember that most schools have specific services to help students with their writing.
- Following the steps of the writing process helps students complete any writing assignment more successfully.
- To manage writing assignments, it is best to work backward from the due date, allotting appropriate time to complete each step of the writing process.
- Setting concrete long- and short-term goals helps students stay focused and motivated.
- A variety of resources are available to help students with writing and with other aspects of post-secondary life.

