7.2: Graphic Organizers
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
Lesson Plan Resources |
|
|
2-Column Note |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
3-2-1 |
Summarizing Strategy See below |
|
3-Column Note |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
5W & How Organizer |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
5W Model |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
ABC Organizer |
Activating/Vocabulary See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Acrostics |
Teaching Strategy |
|
Analyzing Perspective |
Teaching Strategy/Extended Thinking See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Anticipation Guide |
Activating Strategy |
|
Assessment Prompts |
Formative assessment used to gather evidence of learning at strategic points throughout the lesson, which helps the teacher adjust instruction to meet the needs of the learners. They can be in many formats: Written: Think-Ink-Share, Quick Write, Journal Response, Carousel brainstorm, RAFT, Math problems, Error Analysis Visual: Draw a diagram/sketch, Create a visual symbol, Complete a graphic organizer, Think-Sketch-Share Oral: Think-Pair-Share, Numbered Heads Together |
|
Blog |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
Brainstorm Graphic Organizer |
Activating or Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Categorize Vocabulary |
Activating Strategy |
|
Cause/Effect |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Character Map |
Teaching Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Chart/Diagram |
Activating Strategy |
|
Classification |
Grouping items into definable categories on the basis of their attributes (Extended Thinking) |
|
Compare/Contrast |
See attached Graphic Organizer (Extended Thinking) |
|
Concept Definition Map |
Activating/Vocabulary Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Concept Map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Constructing Support |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Creative Design |
Teaching Strategy |
|
Cycle Graph |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Deductive Reasoning |
See attached Graphic Organizer (Extended Thinking) |
|
Descriptive Organizer |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Error Analysis |
See attached Graphic Organizer (Extended Thinking) |
|
Explanation |
Summarize learning |
|
Explanation/process |
Summarize learning based on the process or sequence |
|
Field Notes & Record |
Observe and record data based on observation and/or evaluation of material then summarize findings before progressing to the next level/step |
|
Fishbone Diagram |
Teaching Strategy—Cause/Effect See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Flow chart |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
FRAME |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Frayer |
Activating/vocabulary Strategy |
|
Illustration |
Draw a picture that is a visual representation of the topic. This allows the student to conceptualize the topic and demonstrate understanding. |
|
Inductive Reasoning |
See attached Graphic Organizer (Extended Thinking) |
|
Interpretation |
Summarization strategy |
|
Journal/Journal Entry |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
Justify Your Answer |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
K-W-L |
Activating Strategy |
|
K-W-L Plus |
Activating Strategy |
|
Label & Record |
Activating/Teaching Strategy |
|
Learning/Reflection Log |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
Main idea and Detail map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Main Idea Map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Main Idea Summary |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Matrix |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Mind Map |
Teaching Strategy |
|
Model |
During the lesson, each students labels the model recording their learning with specific details from the lecture, text, video, etc. |
|
Observation Organizer |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
One Sentence Summary |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
Paragraph Summary |
Students use details from graphic organizer or class notes to write a summary in their own words |
|
Pattern Analysis |
Find, identify, and explain patterns within specific skills/concepts/situations |
|
Perform |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
Portfolio Page/Log/Entry |
Examples of student learning |
|
Prediction Guide |
Activating Strategy |
|
Problem Solving Map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Problem/Solution |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Question Quiz Show |
Using any game show format, like Jeopardy Students study/review learned information before an assessment |
|
RAFT |
Summarizing Strategy (see example below) Role of writer: Who are you? Audience: To whom is this written? Format: What form will it take? Topic (+ strong verb): What is the topic? Or What is the time? |
|
Read Aloud |
Teacher READS ALOUD while THINKING ALOUD so students can hear the process needed to solve a problem, interact with text, etc. |
|
Reflective Journal |
Learning Reflection Questions:
|
|
Rephrase |
Summarize Strategy |
|
Role Play |
Summarize Strategy |
|
Sequence Map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
SQ3R |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
SQ4R |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Steps in a Process |
Teaching Strategy See graphic organizer |
|
Story Map |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Story Pyramid |
See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Study Cards |
Summarizing StrategyStudents keep notes based on what they think will appear on the test. Students are able to use their notes during the test. Students can improve their test taking skills and summarizing skills using these study cards. As time goes by, students usefewer and smaller cards until they don’t need any. 1.Determine size of study cards or type of graphic organizer 2.Have students take notes during lesson, readings, video on the cards or graphic organizer |
|
Summarize Details from Graphic Organizer |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
The Absent Student |
Summarizing Strategy |
|
The Important Thing |
Summarizing Strategy (see attached example) |
|
Think Aloud |
Teacher thinks aloud during a read aloud, solving a problem, performing an experiment, etc. so students experience the mental processing needed to solve or interact |
|
Ticket Out the Door |
Summarizing Strategy (see below and attached) |
|
Translation |
Summarization strategy |
|
Video Clip |
Great way to Launch/Activate a unit or lesson (United Streaming contains a variety of video clips. Discoveryeducation.com) |
|
Word Detective |
Vocabulary Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Word Sort |
Vocabulary Strategy See attached Graphic Organizer |
|
Word Splash |
This strategy helps to build relationships between words and key concepts. Students make predictions about what a word means in relationship to the topic. 2.Introduce topic 8.Using Cooperative Learning, have students discuss their sentences and corrections about the information. See attached Vocabulary Graphic Organizer |
|
Word Web |
See attached Vocabulary Graphic Organizer |
2-Column Notes |
|
|
Connections or Cue Column-You might record one or more of the following: *Categories Ex:Causes of WWII Ex: Parts of a Cell *Questions Can write a question that corresponds to the 2ndcolumn *Vocabulary Words Ex: Holocaust Ex: Synthesis *Review/test alert *Connections Ex: Check the Owens poem for his comments on war *Reminders Sample Question and Notes Leave space in the Connections column so you can add notes and test review questions later |
Note-taking Column Write down only important information. Look for: *bold, underlined, or italized words How can I take notes faster? *abbreviate familiar words/use symbols |
|
Summary: Write a Summary of what you read, lecture, the most important points of the article/chapter/lecture |
|
3-2-1
|
3 Things You Found Out |
|
2 Interesting Things |
|
1 Question You Still Have |
3-Column Notes
|
Question |
Answer |
Example(s)/Picture/Symbol |
|
|
5W and How Model
Topic: ___________________________________
|
Who: |
|
What: |
|
When: |
|
Where: |
|
Why: |
|
How: |
|
Summary Statement: |
5W Model
|
Topic: |
|
Who: |
|
What: |
|
When: |
|
Where: |
|
Why: |
|
Summary: |
ABC Organizer
Topic:___________________________
|
A |
G |
M |
S |
|
B |
H |
N |
T |
|
C |
I |
O |
U |
|
D |
J |
P |
V |
|
E |
K |
Q |
W |
|
F |
L |
R |
XYZ |
Analyzing Perspectives
|
Issues |
|
Personal Perspective or Character’s Perspective |
|
Reason/Logic |
|
Different Perspective |
|
Reasons / Logic |
|
Conclusion / Awareness |
Anticipation/Reaction Guide
(Pre-Reading Activity)
An Anticipation/Reaction Guide is used to assess a class’s knowledge before they begin a lesson.
Directions: Respond to each statement twice: once before the lesson and again after reading it.
- Write A if you agree with the statement.
- Write D if you disagree with the statement.
|
Response Before Lesson |
Topic: Dinosaurs |
Response After Lesson |
|
Dinosaurs are the most successful group of land animals ever to roam the Earth. |
||
|
Paleontology is the study of fossils. |
||
|
Human beings belong to the Zenozoic Era. |
||
|
Most dinosaurs have Greek names. |
||
|
Some dinosaurs are named for places in which their fossilized remains were found. |
||
|
Dinosaurs ruled our planet for over 150 million years. |
||
|
Dinosaurs had small brains. |
The statements for the Anticipation/Reaction guide are selected or formed by the teacher based upon significant information in the reading. This activity allows students to focus on some of the important information and see if their Agree/Disagree statements are supported by the reading.

Cause and Effect

Character Map (Literary Element)

-
Write character’s name in central square.
-
In the rectangles, list adjectives or qualities that describe that character.
-
In the ovals, writs examples from the text that support the adjectives or qualities.
Classifying/Categorizing

Compare / Contrast With Summary

Concept Definition Map

Constructing Support

Cycle Graphic Organizer

Deductive Reasoning Graphic Organizer

Directions: Students read and note details, facts, proof Read, gather details, facts, proof and make predictions Make conclusion or final prediction
Descriptive Organizer / Main Idea

Error Analysis
|
What is the information? |
|
Possible errors or clarification of reasoning: |
|
Considered solution or consequence: |
|
New or revised information: |
Fish Bone (Cause / Effect)
Cause

Flow Chart
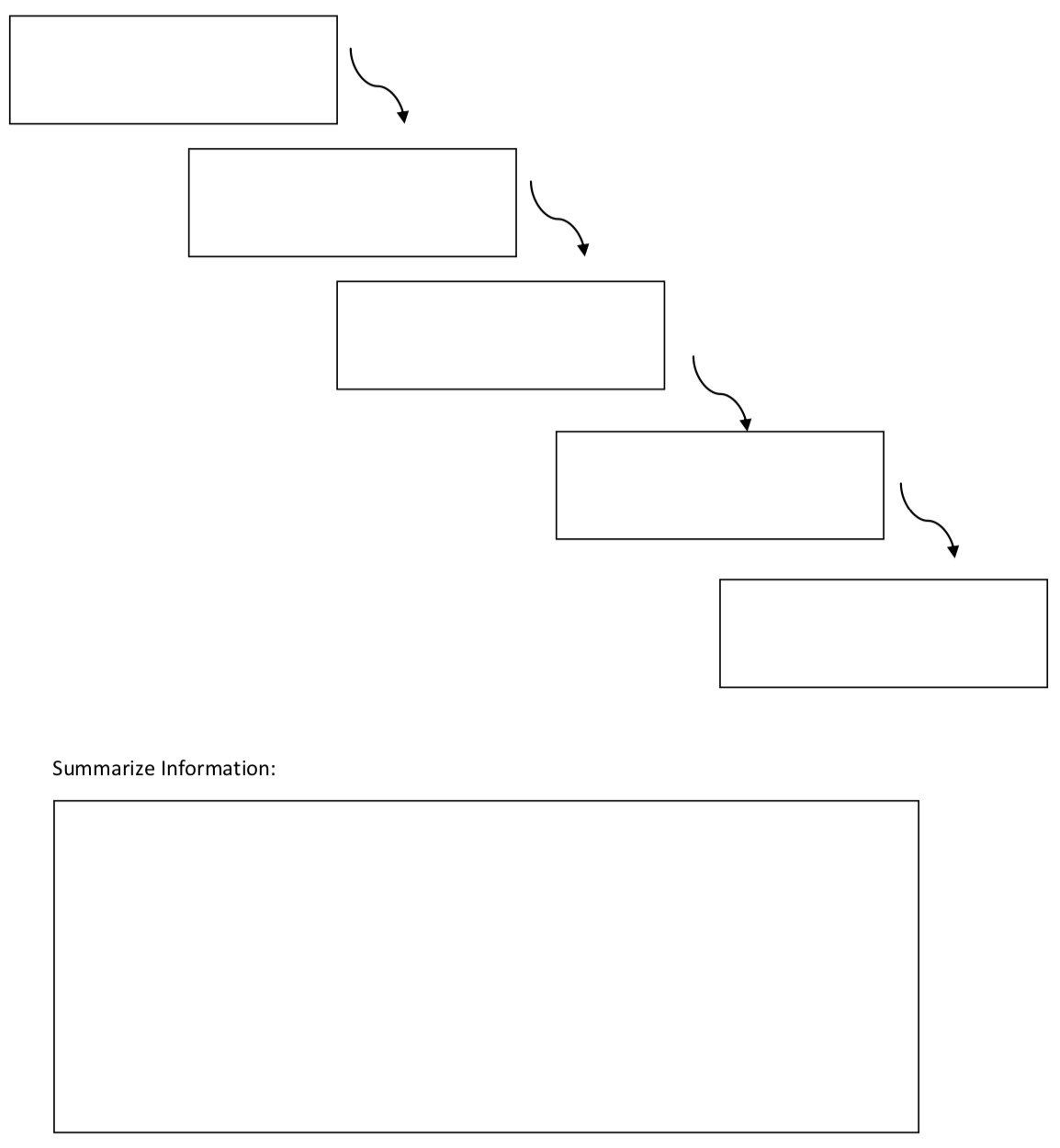
Frayer Diagram 1
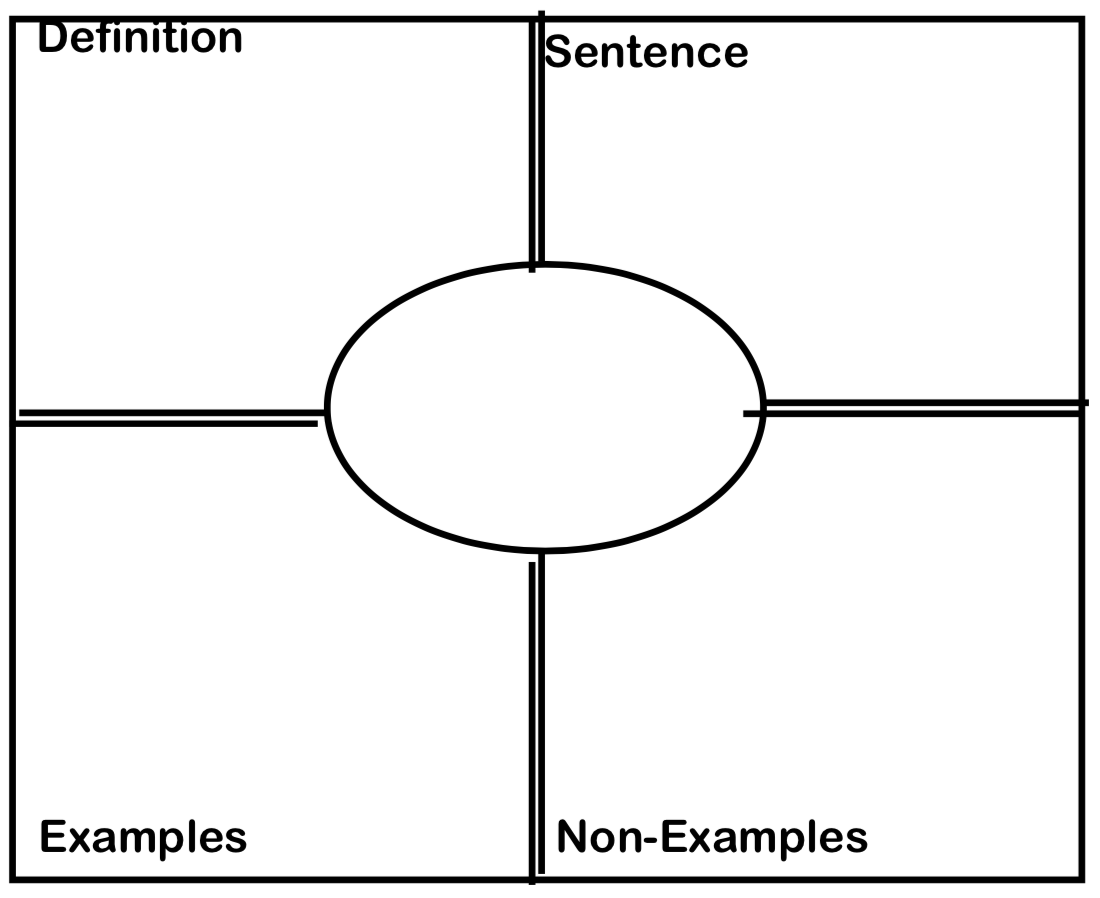
Inductive Reasoning

|
Justify Your Answer |
|
To solve this problem, first I
|
|
Then, I
|
|
The answer is
Because
|
|
Justify Your Answer |
|
To solve this problem, first I |
|
Then, I
|
|
The answer is
Because
|
KWL Examples
|
K |
W |
L |
|
|
KWL
|
K |
W |
L |
|
|
KWL Plus
|
K |
W |
Learned... |
|
|
||
|
Categories for “L” (Learned information) and facts/information within each category |
||
DETAILS (Main Idea)
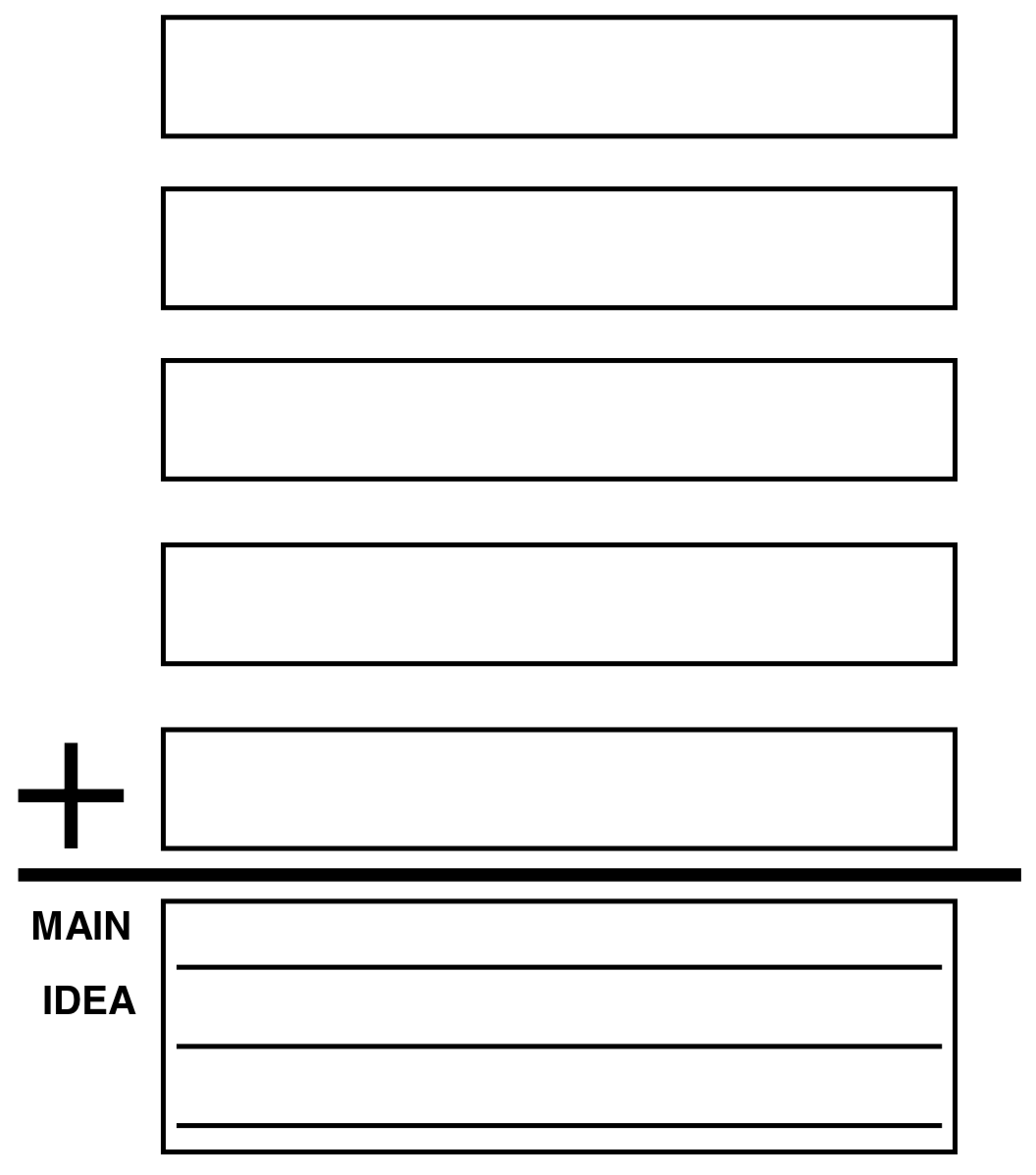

MATRIX (Compare / Contrast Several Items)

Observation Graphic Organizer

|
What is the question? |
|
What is the essential information?
|
|
What is not needed? |
|
What strategy will I use? |
|
Does my answer make sense? |
|
Can I draw a diagram of the problem/solution?
|
Problem/Solution Organizer

RAFT Summarizing Strategy
R.A.F.T. is an activity that allows you to write and express your learning in a creative style.
|
R Role of writer: Who are you? |
A Audience: |
F Format: |
T Topic: |
|
|
|
|
Directions:
-
Select a role, the audience, a format, and a topic from the above list
-
Use the information that you have gathered from our class notes and any of the learning labs for this writing assignment
-
Be Creative! Create the letter, diary entry, warning or brochure about the topic of your choice
Sequence Map




Steps in a Process
|
Topic: |
|
Step 1 |
|
Step 2 |
|
Step 3 |
|
Step 4 |
|
Step 5 |
|
In conclusion, |

Story Pyramid (Characterization)

Directions:
-
Insert 1 word that names a central character.
-
Insert 2 words that describe the setting.
-
Insert 3 words that describe a character.
-
Insert 4 words that describe one event.
-
Insert 5 words that describe another event.


|
Word Sort |
||||
|
Category 1 |
Category 2 |
Category 3 |
Category 4 |
Category 5 |
-
Sort the vocabulary cards
-
Think! What do certain words have in common?
-
Based on those common characteristics, what categories can you add at the top of the column?
-
Sort the vocabulary words based on those common characteristics
-
Write a summary that explains the categories and the common characteristics
-
Read your text to verify or confirm your predictions and/or thought processes

Word Splash
Write the words in random order in any direction around the topic.






