49. La voz pasiva / The Passive Voice
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
| En la voz activa, un sujeto realiza una acción sobre un objeto o complemento directo. | En la voz pasiva, el objeto directo funciona como sujeto, la acción es recibida (ser + participio) y el agente (sujeto activo), si desea mencionarse, aparece después de la preposición por. |
 |
|
| In the active voice, both in English and in Spanish, a subject performs an action on a direct object. | In the passive voice, the direct object functions as a subject, the action is received (be + past participle), and the agent (active subject), if mentioned, comes after the preposition by. |
Ser + participio
 |
| Ejemplos: | |
| El príncipe Felipe fue proclamado rey en 2014. Los mensajes siempre eran enviados a tiempo. Esa canción fue compuesta por la chilena Violeta Parra. La solicitud de ella va a ser aceptada. El amor es deseado por todos. Los bosques están siendo destuidos rápidamente. |
Prince Philip was proclaimed King in 2014. The messages were always sent on time. That song was composed by the Chilean Violeta Parra. Her application is going to be accepted. Love is desired by everyone. Forests are being destroyed rapidly. |
| • El participio funciona como adjetivo, y concuerda en género y número con el sujeto: amor → deseado • mensajes → enviados • canción → compuesta |
• the past participle, as an adjective, must agree in gender and number with the subject): amor → deseado • mensajes → enviados • canción → compuesta |
| • Recuérdese que, cuando hacemos generalizaciones, el sujeto de la oración debe incluir un artículo (u otros determinantes, ver §14): El amor es... • Los bosques están... • El español es... |
• Remember that, unlike English, general subjects must be preceded by an article (or some other determiner, see §14): El amor es... (Love is...) • Los bosques están... (Forests are...) |
| ► Para repasar la formación del participio y el uso de estar con participios (condición resultante), ver §33. |
¡A practicar!
Complete las oraciones con el verbo ser en pretérito y el participio del verbo entre paréntesis. [Ejercicio interactivo] (Diccionario).
Ejemplo: El paciente fue examinado por numerosos especialistas. (examinar)
1. Las islas del Caribe _____________________________ por Cristóbal Colón en 1492. (explorar)
2. Ese problema ______________ por el gobierno el año pasado. (resolver)
3. Durante la colonia, muchos africanos ____________________ como esclavos. (vender)
4. El secreto no _____________________ hasta hace poco tiempo. (revelar)
5. Nuestra casa _____________________ por una famosa arquitecta mexicana. (construir)
6. Todos nosotros ____________________ por la policía después del accidente. (interrogar)
7. La ciudad de Lima _____________________ en 1535 por Francisco Pizarro. (fundar)
8. Las minas de plata de Potosí, en Bolivia, _________________ en 1545. (descubrir)
9. El Paraguay _________________ por tropas brasileñas entre 1870 y 1876. (ocupar)
- Traducción al inglés
- 1) The Caribbean islands were explored by Christopher Columbus in 1492. 2) That problem was solved by the government last year. 3) In the colonial era, many Africans were sold as slaves. 4) The secret was not revealed until not much time ago. 5) Our house was built by a famous Mexican architect. 6) All of us were interrogated by the police after the accident. 7) The city of Lima was founded in 1535 by Francisco Pizarro. 8) The silver mines in Potosí, Bolivia, were discovered in 1545. 9) Paraguay was occupied by Brazilian troops between 1870 and 1876.
- Respuestas
- 1) fueron exploradas - 2) fue resuelto - 3) fueron vendidos - 4) fue revelado - 5) fue construida -
6) fuimos interrogados - 7) fue fundada - 8) fueron descubiertas - 9) fue ocupado
Voz pasiva con se
| La forma más común de construcción pasiva –que algo ocurre, sin indicar quién en particular lo hace–, es con el pronombre se + verbo conjugado en tercera persona singular o plural, en la llamada "pasiva refleja": Aquí se habla español. Se necesita paciencia. ¿Se vivía bien allí? No se puede viajar a otro país sin pasaporte. Esa expresión ya no se usa. Esas expresiones ya no se usan. En Europa no se conocían los tomates antes de 1492. Ya no se producen artículos duraderos. Las instrucciones se tenían que seguir (tenían que seguirse). Esa ley se va a revocar (va a revocarse). En este tipo de construcción normalmente no se nombra el agente. Esa expresión no se usa en Colombia. Esa expresión no es usada por los colombianos. Y es común en avisos impersonales: Se busca empleado. Se venden productos lácteos. Se hacen reparaciones. No se puede entrar. |
The most common form of passive construction in Spanish –that something happens, but without expressing who in particular does it–, is by using se + a verb conjugated in the third person (singular or plural). Spanish is spoken here. You need patience (patience is needed). Did one live well there? (was life good there) One cannot travel to a different country without a visa. That expression is not used (in use) anymore. Those expressions are not used anymore. Tomatoes were not used in Europe before 1492. Durable articles are not produced anymore. Directions had to be followed. That law is going to be revoked. Normally, do not try to mention the agent with the passive se: That expression is not used in Colombia. (se is fine) That expression is not used by Colombians. (use ser) And it is common in impersonal announcements: Employee needed (sought). Milk products sold (here). Repairs made. It is not possible/allowed to enter/come in. |
| • Para no especificar quién realiza una acción, también es frecuente el uso de una tercera persona del plural, genérica, sin el pronombre: En mi ciudad respetan al peatón. (o: se respeta al peatón). Aprobaron la ley esta mañana. (o: la ley se aprobó esta mañana). |
• Similar to English, Spanish can also use an impersonal They..., without the subject pronoun: They respect pedestrians in my city. (or: pedestrians are respected) They approved the law this morning. (or: the law was approved) |
¡A practicar!
Complete las oraciones con se y el imperfecto del verbo indicado. [Ejercicio interactivo] (Diccionario).
Ejemplo: El paciente esperó mientras se estudiaba su caso en el hospital. (estudiar)
1. En la época colonial no siempre _____________________________ las leyes dictadas en España. (obedecer)
2. Por ejemplo, oficialmente solo ______________ comerciar con Madrid, (permitir) ...
3. ... pero con frecuencia ____________________ muchos productos con otros países europeos. (traficar)
4. También _____________________ muchos libros prohibidos. (publicar)
5. Según la ley, los resguardos indígenas _____________________ que respetar, (tener) ...
6. ... pero muchos de ellos ____________________ para la agricultura o la minería. (invadir)
7. En Madrid _____________________ muchas leyes para proteger a los ciudadanos, (expedir) ...
8. ... pero en América _________________ pocas de esas leyes. (implementar)
- Traducción al inglés
- 1) In the colonial era, the laws dictated in Spain were not always obeyed. 2) For example, officially, it was only allowed the trading with Madrid, 3) but many products were often trafficked with other European countries. 4) Many forbidden books used to be published as well. 5) According to the law, Indian reservations had to be respected, 6) but many of them were invaded for agriculture or mining. 7) In Madrid, many laws were issued to protect citizens, 8) but few of those laws were implemented in America.
- Respuestas
- 1) se obedecían - 2) se permitía - 3) se publicaban - 4) se publicaban - 5) se tenían - 6) se invadían - 7) se expedían - 8) se implementaban
Se + objeto indirecto
| Como se explicó arriba, la voz pasiva convierte al objeto directo en sujeto: | As explained above, passive voice turns the direct object into the subject: |
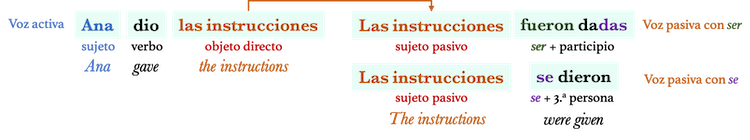 |
|
| Si hay objeto indirecto, el pronombre va después de se: | If there is an indirect object, place its pronoun after se: |
 |
|
| El orden de los elementos es flexible, con las siguientes posibilidades: Las instrucciones se le dieron al portero. Al portero se le dieron las instrucciones. Se le dieron las instrucciones al portero. La tercera es la más común. Más ejemplos: Se le mandaron flores (a ella). Se te dieron opciones (a ti). (Te dieron opciones). Se les dijo cómo hacerlo. (Les dijeron cómo). Se me permitió entrar (me permitieron entrar). Se nos invitó a participar (nos invitaron a participar). |
The word order is flexible, and is roughly equivalent to the "false passive" in English, that is, a construction that uses the indirect object (to whom?) as the subject: The doorman was given the directions (they were given to him). More examples: She was sent flowers (flowers were sent to her). You were given options (options were given; they gave you options). They were told how to do it. I was allowed to enter (they allowed me to enter). We were invited to participate (they invited us to). |
| Esta misma estructura (se + pronombre de objeto indirecto) se emplea con un grupo limitado de verbos para indicar acciones no deliberadas, expresando que algo ocurre por accidente. El se pasivo señala un acontecimiento no planeado, el pronombre de objeto indirecto (me, te, le, nos, os, les) indica la persona afectada por el suceso, y el verbo se conjuga en tercera persona del singular, en concordancia con las cosas perdidas, olvidadas, etc.: Se les olvidó la cita. ¿Se te perdieron las llaves? A mí no. Se nos acabó la gasolina. Al carro se le dañaron los frenos. No tengo el libro: se me quedó en casa. Mira, se te cayeron las llaves. A Juan se le rompió el pantalón al sentarse. Se les quebraron los platos durante la mudanza. Llegas tarde, ¿se te descompuso el reloj? Se me confunden los datos. Para expresar que una idea viene a la mente de forma repentina o inesperada, se emplea esta misma construcción con el verbo ocurrir: Se nos ocurrió una idea brillante. No se me ocurre nada para resolver ese problema. |
This same structure (se + indirect object pronoun) is used with a limited group of verbs to indicate non-deliberate actions, conveying that something happened by accident. The passive se indicates that the event was unexpected; the object pronouns (me, te, le, nos, os, les) indicate the person(s) affected by the event; and the verb uses the third person singular or plural to agree with the things lost, forgotten, etc. They forgot (about) the appointment. Did your keys got lost (on you)? Not mine (to me). We ran out of gas. The car's brakes got damaged. I don't have the book. I left it home (accidentally). Look, you dropped the keys (involuntarily). Juan's pants tore when he sat down. Their dishes broke during the move. You're late, did your watch broke (on you)? The data are confused in my mind. "To occur to someone" in the sense of getting a sudden idea or impression is expressed by ocurrir in this kind of construction: We just got a brilliant idea. Nothing occurs to me (I can't think of anything). |
| ⇒ Do not try to express it or them with the structures above. If you must, it will have to be with an appropriate demonstrative pronoun (acting as subject): I dropped it: Se me cayó. Se me cayó eso. (I dropped that). - She forgot them: Se le olvidaron. Se le olvidaron estas. (She forgot those ones). |
¡A practicar!
Complete con se, el pronombre de objeto indirecto (me, te, le, nos, os, les) apropiado y el pretérito del verbo indicado. [Ejercicio interactivo] (Diccionario).
Ejemplo: Me confundí con los datos. A mí se me confundieron los datos.
1. No me dieron la información. A mí no ________________ la información correcta.
2. Mira, dejaste caer un libro. A ti ________________ este libro en el pasillo.
3. A ella le dijeron qué hacer. ________________ lo que necesitaba hacer.
4. Nunca olvidamos su cumpleaños. Y el año pasado tampoco ________________ la fecha.
5. ¿Os permitieron expresar vuestras opiniones? ¿________________ expresaros libremente?
6. Ellos siempre pierden todo, pero afortunadamente ayer no ________________ nada.
7. Olvidé decir muchas cosas en la presentación. ________________ las ideas por los nervios.
8. Esa taza se quebró por accidente. A José ;_________________ la taza mientras lavaba los platos.
- Traducción al inglés
- 1) They didn't give me the information. I was not given the correct information. 2) Look, you dropped a book. This book fell off you in the hall. 3) They told her what to do. She was told what she needed to do. 4) We never forget her birthday. And last year we didn't forget the date, either. 5) Did they let you all express your opinions? Were you allowed to express freely. 6) They always lose everything, but fortunately they didn't lose anything yesterday. 7) I forgot to say many things during the presentation. I forget the ideas because of the nerves. 8) That cup broke by accident. José broke the cup while doing the dishes.
- Respuestas
- 1) se me dio - 2) se te cayó - 3) se le dijo ;- 4) se nos olvidó ;- 5) se os permitió ;- 6) se les perdió - 7) se me olvidaron - 8) se le quebró
Práctica interactiva
• ASCCC: usos comunes de se
• aprenderespañol: la voz pasiva, nivel 1 - la voz pasiva, nivel 2
• ver-taal: frases pasivas e impersonales con se (texto sobre los masái)


